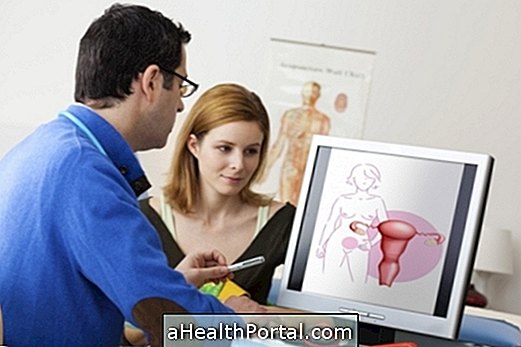
Examination of the cervix is usually done primarily by performing a pap smear, which is simple and painless, and is important for all women, especially women of childbearing age. This test should be done annually to identify changes in the cervix and prevent the onset of cancer.
In cases where the pap smear indicates the presence of changes in the cervix of the woman, these are in most cases not cancer, but must be diagnosed and treated in advance. In these cases, the doctor should ask for more specific exams to the cervix, such as colposcopy or biopsy of the cervix.
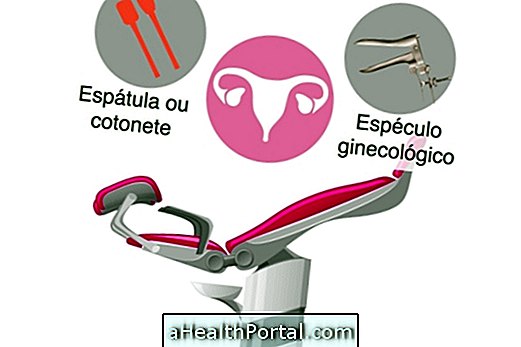
How is the cervix done?
Examination of the cervix is done by performing a cytopathological examination also known as a pap smear, where a small sample of vaginal secretion and cervical cells are collected using a swab or a spatula. The collected sample is then sent by the physician to the laboratory, and the result of the test comes out in a few days.
This exam is a quick procedure, which does not cause pain, only a slight discomfort. After the test, no symptoms are expected and no special care is needed, but if you experience discomfort in the pelvic area after the examination or if you bleed for more than one day, you should consult your doctor.
During pregnancy, this test can also be done according to the gynecologist's instructions, and it must be done carefully and may cause a slight bleeding.
What is the purpose of the examination of the cervix
The examination of the cervix serves to:
- Help identify early changes in the wall of the cervix, which can progress to cervical cancer, since these changes when detected early can easily be treated.
- to identify Naboth cysts, a benign change common in many women;
- Helps detect other gynecological inflammations, warts or other sexually transmitted diseases. See what this Pap smear looks like.
- It helps identify cell changes that suggest the presence of the HPV virus, because although it does not allow diagnosis, it helps to identify suspicions of the virus.
See more on what factors can increase cancer risk in: HPV and cervical cancer.
Pap smear results
The pap smear may give a negative or a positive result, which indicates whether or not there are changes in the woman's uterine wall. When the result of the test is negative, it indicates that there are no changes in the wall of the woman's uterus, so there are no signs of cancer.
On the other hand, when the result of the pap smear is positive, it indicates that there are changes in the woman's uterine wall, and in these cases the doctor will recommend more specific exams such as colposcopy to identify the problem and treat it.
When to perform colposcopy and biopsy of the cervix
Colposcopy is done whenever the pap smear is positive and indicates changes in the cervix. In this examination, the doctor applies a dye solutions in the uterus and observes using a device called a colposcope, which has lighting and magnifying glasses, acting as a kind of magnifying glass. See how this Colposcopy exam is done.


When colposcopy indicates the presence of changes in the uterine wall, the doctor will then request an examination of a histopathological examination of the cervix, which consists of a biopsy of the cervix, where a small procedure is performed to collect a small sample of the uterus, which is then analyzed by the doctor. This test is only done when there is strong suspicion of changes in the woman's cervix.