Limb tendonitis occurs when there is a deposition of small calcium crystals in a tendon.
It is not yet known exactly why this calcification is formed but the most accepted theory is that it forms due to the decrease of blood that reaches the inflamed tendon, and there is a deposition of calcium salts in that place. Changes in thyroid and estrogen metabolism may also favor its formation.
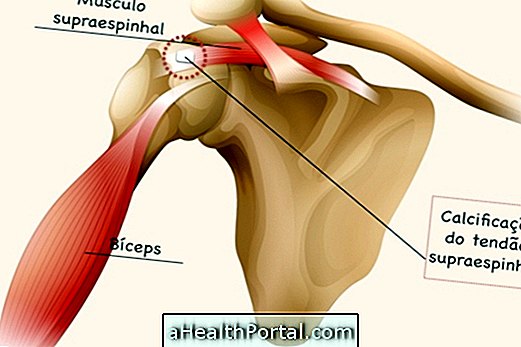
It usually forms after the age of 40 and is more common in women, and although it may appear on only 1 side of the body, it can also affect both at the same time. One of the most affected tendons is the supraspinatus tendon, as shown in the image above, but the rotator cuff of the shoulder is also very affected.
How to identify a calcification in the tendon
The only way to identify a calcification in a tendon is through imaging tests. The x-ray should not show the tendon, however, in case of calcification a small white area can be seen where it formed.
When palpating the tendon, the person should feel some pain, but it is not possible to affirm that there is calcification only because of the pain and therefore an examination of image can be useful, although normally it is not requested only by this suspicion.
How to treat limb tendonitis
Calcium tendonitis cures on its own because there is a spontaneous remission of bone deposition, however, it is not known when this happens and so whenever the person presents symptoms he must perform the treatment with some sessions of physiotherapy, often using electrotherapy, to decrease the inflammation and pain of surrounding tissues.
Analgesics and anti-inflammatories in tablets or ointments may also help to combat pain, but in some cases arthroscopy surgery is more efficient, this consists of a scraping of the calcified site, completely eliminating calcification. Infiltrations with anesthetics and corticosteroids are also indicated to relieve pain immediately, but can only be performed 1 to 2 times a year.
Here are some quick tricks to combat pain in the following video:

Physiotherapy for limb tendinitis
The resting of the affected limb is indicated when there is pain and limitation of movement and so whenever possible avoid heavy objects with the affected arm, for example. However, there is no need for absolute rest and therefore the use of sling is inadvisable because it is important to maintain some movement to maintain the production of synovial fluid that irrigates the joint.
In physical therapy TENS and ultrasound are indicated for the control of pain although it is not yet known exactly how the ultrasound acts in the reabsorption of the deposited calcium it increases the temperature of the place and the blood flow, facilitating the removal of the deposits of calcium.
Exercises such as stretching and muscle strengthening with elastic bands like Theraband are indicated as well as joint manipulation techniques. Pendulum exercises are excellent strategies to decrease pain and maintain capsule integrity by preventing the shoulder protection position, which generates more pain and restriction of movement.