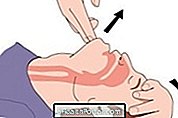
Mouth-to-mouth breathing becomes important and necessary in cases of:
- Cases of drowning
- Trauma cases
- Children and babies
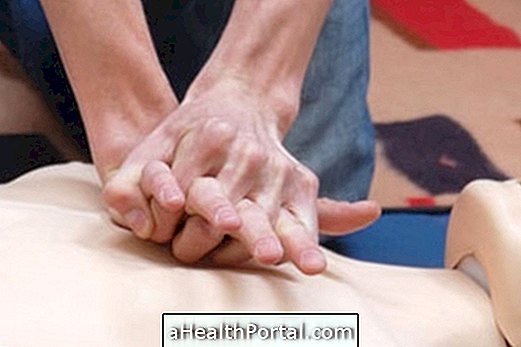
Studies have shown that firm, rhythmic heart massage is sufficient to keep the victim alive until professional relief arrives without the use of mouth-to-mouth resuscitation.
In the case of children and infants, drowning or trauma, in addition to cardiac massage, it is necessary to perform mouth-to-mouth breathing at the rate of 2 breaths (ventilations) for every 30 chest compressions. However, in other situations of cardiac arrest, cardiac massage should be given priority, until rescuers arrive to take the victim to the hospital.