Anemia is a disease characterized by decreased hemoglobin in the bloodstream, which can have several causes, from a genetic change to poor diet. They usually produce similar symptoms such as dizziness, pallor, headache, weakness, dry skin and mucous membranes.
To identify and confirm the diagnosis of anemia, the doctor usually asks for a blood test to evaluate the amount of hemoglobin, and is considered anemia when the value is less than 12 g / dL in women or 13 g / dL in men. Further tests, such as hemoglobin electrophoresis, reticulocyte counts or stool examination, may be necessary to identify the correct type of anemia and initiate appropriate treatment.
Whatever the anemia the individual possesses, she needs treatment. That's because when untreated, they can develop complications that result in irreversible brain damage, such as dementia, stroke and cardiovascular problems, for example. Thalassemia is also a type of anemia, but it is genetic and has no cure. Here's how to identify thalassemia.
1. Iron deficiency anemia
It is one of the most common types of anemia, which is caused by low consumption of iron foods such as red meat, egg or spinach. However, this type of anemia can also occur after bleeding or severe menstruation, due to loss of iron by the blood.
How to treat : It is usually treated with a food rich in foods with iron and iron supplementation. Only in the most severe cases is it necessary to have a blood transfusion. Learn more about this type of anemia and how to treat it.
2. Megaloblastic anemia
It is a type of anemia characterized by the abnormal size of red blood cells and decreased white blood cells and platelets, caused by the low intake of vitamin B12, more common in vegetarians. In addition to the classic symptoms, there may be pain in the belly, hair loss, tiredness and mouth sores, for example.
How to treat : Increased intake of foods with vitamin B12, such as oysters, salmon and steak liver or use of vitamin B12 supplements, purchased from the pharmacy. Understand better how the treatment is done.
3. Pernicious anemia
This is a type of megaloblastic anemia that occurs when the person ingests vitamin B12, but the body can not absorb it and can result in severe neurological damage if treatment is inadequate.
How to treat : Due to the difficulty in absorbing vitamin B12, treatment should be done with vitamin injections directly into the vein throughout the year. Discover how to identify and treat pernicious anemia.
Learn more about pernicious anemia in the following video:

4. Hemolytic anemia
This type of anemia produces antibodies that destroy blood cells. It is more common in women than in men and causes symptoms such as pallor, dizziness, purple marks on the skin, dry eyes and skin, and others. See other symptoms of this type of anemia.
How to treat : Fortunately, this anemia has a cure and this can be achieved with the use of corticosteroids or immunosuppressive medicines. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove a part of the spleen.
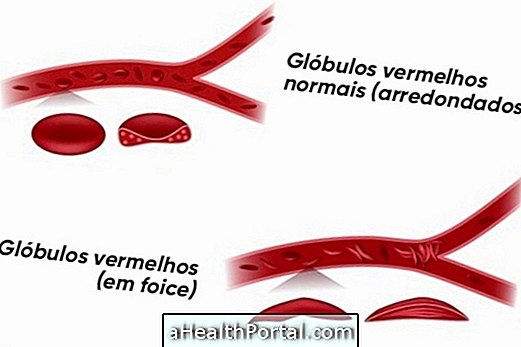
Sickle cell anemia
It is a genetic anemia caused by the destruction of red blood cells which generates symptoms such as jaundice, swelling in the hands and feet and pain throughout the body.
How to treat : The treatment is made with medicines to relieve the symptoms of each person, since there is no treatment capable of curing this type of anemia. Learn more about sickle cell anemia and the different treatments used.
6. Aplastic anemia
It is an autoimmune disease where the bone marrow decreases the production of blood cells, causing symptoms such as purple spots on the skin, frequent bruising and bleeding that take a long time to stop. Understand this type of anemia better, diagnosis and treatment.
How to treat : Your treatment is done with bone marrow transplantation and blood transfusion, when not properly treated, can lead to death in less than 1 year.
7. Anemia of Fanconi
It is another type of genetic anemia characterized by abnormal red blood cell size and decreased white blood cells and platelets, caused by vitamin B12 deficiency. Symptoms include belly pain, hair loss, tiredness and mouth sores, for example.
How to treat : Treatment usually begins with the use of corticosteroids, but blood transfusions and even bone marrow transplantation may be needed in more severe cases. Learn more about the types of treatment.