Intoxication is the set of signs and symptoms caused by exposure to chemicals harmful to the body, such as overdoses, stings from poisonous animals, heavy metals such as lead and mercury, or exposure to insecticides and pesticides.
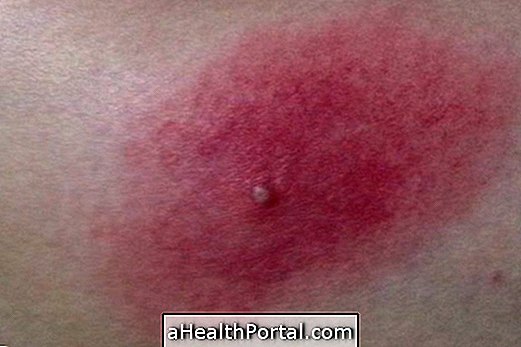
Intoxication is a form of poisoning, and can cause local reactions such as redness and skin pain, or systemic, such as vomiting, fever, intense sweating, seizures, coma, and even death. Therefore, in the presence of signs and symptoms that indicate this problem, it is important to go to the emergency room quickly, so that the treatment is done, with gastric lavage, use of medicines or antidotes, prescribed by the doctor.
Types of poisoning
There are different types of poisoning, such as:
- Exogenous intoxication : occurs when the substance intoxicating is in the environment, able to contaminate through ingestion, skin contact or inhalation through the air, and the most common are the use of drugs in high doses, such as antidepressants, analgesics, anticonvulsants or anxiolytics, use of illicit drugs, poisonous animal stings such as snakes or scorpions, excessive alcohol consumption or inhalation of chemicals, for example;
- Endogenous poisoning : it is caused by the accumulation of harmful substances that the organism itself produces, such as urea, but which are usually eliminated through the action of the liver and filtering through the kidneys, and can be accumulated when these organs have insufficiency.
In addition, intoxication can be acute, when they cause signs and symptoms after a single contact with the substance, or chronic, when their signs are felt after accumulation of the substance in the body, consumed for a long time, as in drug poisonings such as Digoxin and Amplictil, for example, or metals such as lead and mercury.
Gastroenteritis, also known as food poisoning, occurs due to the presence of microorganisms such as viruses and bacteria, or their toxins, in food, especially when poorly preserved, causing nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. To learn more about this situation, see how to identify and treat food poisoning.
Main symptoms
As there are several types of toxic substances, there are a wide variety of signs and symptoms that may indicate intoxication, and some of the major ones are:
- Accelerated or slow heartbeat;
- Increased or decreased blood pressure;
- Increased or decreased pupil diameter;
- Intense sweating;
- Redness or injury to the skin;
- Visual changes such as blurring, blurring or dimming;
- Shortness of breath;
- Vomiting;
- Diarrhea;
- Abdominal pain;
- Somnolence;
- Hallucination and delirium;
- Urinary and fecal retention or incontinence;
- Lentifying and difficulty performing movements.
Thus, the type, intensity, and amount of intoxication symptoms vary depending on the type of toxic substance that is ingested, the amount and physical state of the person who ingested it. In addition, children and the elderly are more sensitive to poisoning.

First aid for intoxication
First aid that should be done in a poisoning case include:
- Immediately call SAMU 192, ask for help and then to the Antivenus Information Center (CIAVE) , on 0800 284 4343, to receive guidance from the professionals while the medical help arrives;
- Remove toxic agent, wash with water if in contact with skin, or change environment if inhaled;
- Keep the victim lying in a lateral position if they lose consciousness;
- Look for information about the substance that caused intoxication, if possible, such as checking the box of medicines, containers of products or the presence of venomous animals nearby, to help inform the medical staff.
Drinking liquids or vomiting should be avoided, especially if the substance ingested is unknown, acidic or corrosive, as this may worsen the effects of the substance in the digestive tract. To learn more about what to do in the event of poisoning or poisoning, check out first aid for poisoning.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for intoxication varies according to the cause and the person's clinical condition. It can be initiated either in the ambulance or upon arrival at the emergency room by the medical staff and involves:
- Assessment of vital signs, such as pressure, heart rate and blood oxygenation, and stabilization, with hydration or use of oxygen, for example if necessary;
- Identify the causes of intoxication, through the analysis of the clinical history, symptoms and physical examination of the victim;
- Decontamination, which aims to reduce exposure of the body to the toxic substance, through measures such as gastric lavage, irrigation of saline solution through a nasogastric tube, administration of activated charcoal in the digestive tract to facilitate the absorption of the toxic agent, or intestinal lavage with laxatives such as mannitol;
- Use an antidote, if any, that may be specific to each type of substance. Some of the most commonly used antidotes are:
| Antidote | Intoxicating agent |
| Acetylcysteine | Paracetamol |
| Atropine | Organophosphate insecticides and carbamates, such as Chumbinho; |
| Methylene blue | Substances called methemoglobinizers, which prevent oxygenation of blood, such as nitrates, exhaust gases, naphthalene and some medications, such as Chlorin and Lidocaine, for example; |
| BAL or dimercaprol | Some heavy metals, such as arsenic and gold; |
| EDTA-Calcium | Some heavy metals, such as lead; |
| Flumazenil | Benzodiazepine medicines such as Diazepam or Clonazepam, for example; |
| Naloxone | Opioid analgesics such as Morphine or Codeine, for example |
|
Anti-Corticosic, Anti-Aphid or Antiarachidic Serum | Venomous scorpion, snake or spider bites; |
| Vitamin K | Pesticides or anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin. |
In addition, to avoid any kind of intoxication, it is important to pay attention to the products that come into contact in the day-to-day, mainly people who work with chemicals, such as in factories or plantations, being indispensable the use of protective equipment individual.
Particular attention should also be paid to children, who are more likely to contact or accidentally ingest intoxicants and to suffer domestic accidents. Also check out what first aid is for other common household accidents.