The treatment to correct flat feet can be done with the use of insoles, orthopedic shoes, however, physiotherapy sessions with exercises that help in the formation of the foot cavity besides the practice of exercises may also be necessary.
The flat foot is when the whole sole of the foot touches the ground and a good way to confirm this is after the bath, with the feet still wet, to step on a towel and to observe the drawing of the foot. In the case of flatfoot the foot design is wider, whereas in the normal foot in the middle part the foot, the drawing becomes narrower.

When you need treatment
When the child is less than 8 years old, she does not always need to do any specific treatment to correct flat feet. Up to age 8, it is normal for the child to have a flat foot because the place of curvature may still contain some fat that has been present there since birth.
In consultation with the pediatrician he can observe the feet and how the child walks at 3, 4, 5 and 6 years. Usually from the age of 6 or 7, your pediatrician may recommend an appointment with an orthopedist to decide whether you need to wait longer to see if your foot arch forms alone, or if you need to do any treatment.
The treatment to develop the child's foot arch can be started at age 6, because from that age, the child grows and the accumulation of fat in the foot decreases a lot, evidencing if there is any foot cavity or none at all. Lean children probably do not have 'greasy' foot and so the suspicion of flat feet grows.

Tips for forming the arch of the foot naturally
What can be done to aid in the formation of the child's foot arch is to take it to walk barefoot on the sand of the beach for 20 to 30 minutes daily. In addition, riding a bike and always wearing semi-orthopedic shoes, as long as the child starts walking, is a great help to avoid that the child needs to do a more specific treatment like using insoles, shoes or orthopedic boots and do physiotherapy.
These tips should be followed as soon as the parents notice that the child has flat feet, without any curvature, before the age of 6, but they should be followed even if the child has to do the treatment after the age of 8 years.
It is normal for every child up to 3 years to have flat feet without any curvature on the sole of the foot, but from that stage the curvature should begin to become clearer and more evident. If this does not happen, parents should not fail to follow these tips and always invest in good shoes, especially noting if the internal salad helps in the curvature of the foot, avoiding all those that have the internal soles completely straight, that although they are the most economical and easy to find in children's clothing stores, do not help in the formation of the child's foot arch.
Treatment Options for Flat Foot
Treatments for flat foot in childhood are usually initiated after 6 or 7 years of age with:
Wear orthopedic shoe
In the case of the child with flat feet, the pediatric orthopaedist can indicate the use of an orthopedic shoe because as the foot is still developing the shape of the shoe and the adequate insole help to form the arch of the foot. The child will need the orthopedic shoe every day, but nowadays there are several options such as sandals, sneakers, boots and shoes, full of colors and beauty.
The ideal is to buy the orthopedic shoe indicated by the doctor in a store of orthopedic products because each child has its need and one shoe is not exactly the same as the other, being necessary to take the measurements, and sometimes, it may be necessary to make a custom shoe .

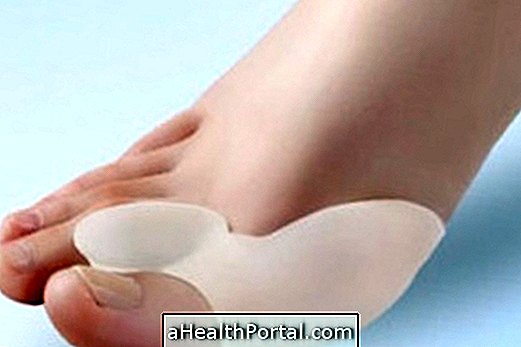
Wear insole in non-orthopedic shoe
A custom insole can be used inside a tennis shoe, for example. The insole should be taller at the heel and have support for the middle of the foot. Although this is an excellent help does not rule out the need to use orthopedic shoe, because this type of shoe is totally made to accommodate the foot properly.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy sessions can be held 1 or 2 times a week, with exercises and manipulations on the foot of the child. Any physiotherapy clinic is able to do this kind of care, but the specialist physical therapist in osteopathy and global postural reeducation can make a thorough evaluation of the whole body of the child, indicating a type of differential treatment that can work not only the feet, but all body posture.
Placing a wide adhesive tape covering the sole of the foot is also a good stimulus to aid in the formation of the plantar arch.
Exercise
Enrolling the child in activities such as Ballet, Artistic Gymnastics or Swimming helps to strengthen the muscles and form the arch of the foot faster. Each child has their own rhythm but it is best that they do this type of activity at least 2 times a week. So that the child does not get sick of the same activity, it can be varied, doing each activity that wishes once a week. Other more specific exercises are:
- Walking on tiptoes and only on the heels;
- Support the weight of the body in only 1 foot and do a squat in that position;
- Hold a marble with your toes and place in a bowl,
- Climb stairs on tiptoe;
- Lie on your belly up and keep the floor of both feet together
When to do surgery
It is indicated to perform surgery to correct the flat foot when the treatment is not effective and the child or adult remains with the flat foot, but it is important to always perform surgery to evaluate the results before resorting to this last resort. The surgery is done in 1 foot at a time and usually several surgical procedures are performed and the person is rested for 1 week, after that it is necessary to do physiotherapy to help in recovery and when this is achieved the surgery can be performed on the other foot. Surgery is only performed on 2 feet at the same time in children, but even then, it is not a common procedure.
What can happen if you do not treat
The arch of the foot serves to help cushion the pressures when walking, running and jumping and so when the person does not have a well formed arch and presents the foot flat, his foot is unprotected and complications can arise over time, such as fasciitis, which is an inflammation in the sole of the foot that causes intense pain; spur that is the formation of a bone callus on the soles of the foot leading to frequent crises of fasciitis, in addition to pain and discomfort in the ankles, knees and hips, for example.