Rhabdomyolysis is a severe syndrome that causes destruction of muscle fibers and may occur after direct or indirect trauma to a muscle in the body.
After their destruction, the muscle fibers release substances toxic to the bloodstream that end up causing serious complications in the kidneys, and can even result in renal failure. Therefore, treatment should be started as soon as possible and go to the emergency room as soon as rhabdomyolysis is suspected.
Main symptoms
Symptoms of rhabdomyolysis are not always easy to identify, however, the most common include:
- Pain in the muscles of the shoulders, thighs or bottom of the back;
- Lack of strength;
- Difficulty in moving legs or arms;
- Urine in small quantity and very dark.
In addition to these symptoms, more general signs such as fever, nausea, abdominal pain, general tiredness, vomiting, confusion and restlessness may also appear.
Since the symptoms vary according to the cause, as well as the body of each person, it can be quite difficult to identify a case of rhabdomyolysis.
How to confirm the diagnosis
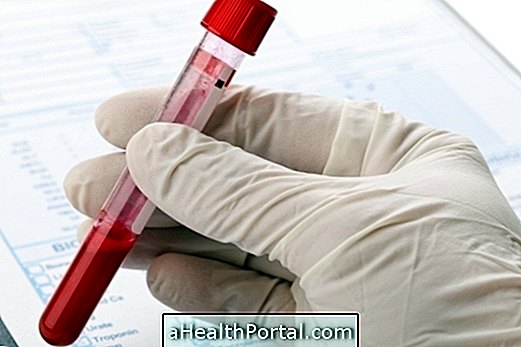
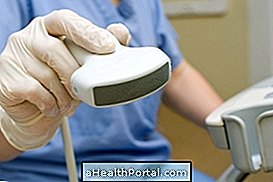
The diagnosis of rhabdomyolysis is usually made by the physician after evaluation of symptoms and clinical history, as well as blood and urine tests to observe the plasma levels of substances such as CK and other muscle enzymes.
Here is an example of an exam that can be used to confirm cases of rhabdomyolysis.
What causes rhabdomyolysis
The main causes of rhabdomyolysis include:
- Excessive muscle strain, caused by very intense physical exercise;
- Serious accidents such as high altitude falls or traffic accidents;
- Prolonged use of some medications, especially antipsychotics or statins;
- Use of drugs, mainly cocaine, heroin or amphetamines;
- Prolonged immobilization due to fainting or illness.
Rhabdomyolysis can also be caused by other problems such as electric shock, stroke, metabolic diseases and viral infections such as herpes or HIV.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for rhabdomyolysis is done at hospital admission with serum injections directly into the vein to avoid serious complications of the disease, such as dehydration or kidney failure, caused by excess muscle wastes in the blood.
In addition, it is important to identify the cause of rhabdomyolysis to initiate appropriate treatment, if necessary. So if it is being caused by the use of some medicine, for example, you should stop taking it and switch to another medicine.
The duration of treatment varies according to the cause and the patient's progress, and during hospitalization it is necessary to stay algalized to assess the amount of urine per day and to perform other renal exams to ensure that kidney function is not being affected. The patient is usually discharged when the tests are normal and there is no risk of developing kidney failure.
In more severe cases, where the kidneys begin to produce little urine, the doctor may prescribe dialysis to help kidney function by eliminating excess blood substances that may be making treatment difficult.
Possible Complications
The most serious and common complication of rhabdomyolysis is the onset of kidney damage, which can lead to kidney failure. However, the presence of residues in the blood also leads to an increase in potassium and phosphorus levels in the body, which can end up affecting the functioning of the heart.
In rarer situations, another syndrome known as compartment syndrome, in which the blood circulation is compromised in a region of the body, such as legs, arms or some muscles of the abdomen, causes death of the tissues.