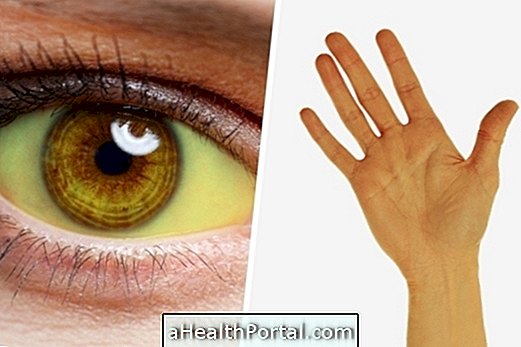
The yellowish skin can be a symptom of various diseases of the liver such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, for example, especially if the person also presents the white part of yellow eyes, in these cases the yellowish skin called jaundice. However, yellow skin may also be a sign of other diseases such as anemia or anorexia nervosa.
In addition, high intake of foods rich in beta-carotene such as carrot or papaya can also cause yellow skin, however, in these cases, the eyes do not turn yellow, only the skin.
If the person has yellow skin and eyes, it is important to go to the emergency room for tests to identify the cause.
Main causes
The yellowish skin can be a symptom of several conditions, the main ones being:
1. Hepatitis
Hepatitis is the most common cause of jaundice and corresponds to inflammation of the liver caused by viruses, continued use of medications or autoimmune disease, leading to symptoms such as yellowing of the skin, abdominal pain and swelling, mild fever, itching, nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite. See what the symptoms of hepatitis are.
What to do: The treatment of hepatitis should be done according to the medical recommendation, and the use of medication or rest, proper nutrition and hydration may be recommended depending on the cause of the hepatitis. Learn all about hepatitis.
2. Hepatic insufficiency
Liver failure occurs when the liver is not able to perform its normal functions such as detoxification of the body, for example. In this case, in addition to jaundice, the person usually exhibits body swelling, body odor, bleeding and ascites which is the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen.
What to do: It is important to consult the hepatologist to establish the best form of treatment, which is usually done through liver transplantation. See when liver transplantation is indicated and how recovery is.
3. Liver cyst
The liver cyst is a fluid-filled cavity in the liver that normally does not produce symptoms, however, in some cases, it can lead to the yellowish appearance of the skin, as well as in the abdomen, sudden weight loss, fever over 38ºC and fatigue.
What to do: Liver cyst usually does not require specific treatment, but if it gradually increases in size and causes symptoms, surgical removal may be necessary. Learn more about liver cysts.
4. Hepatic cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis corresponds to chronic and progressive inflammation of the liver characterized by the destruction of liver cells, which can cause yellow skin and yellow eyes, whitish nails, bad breath, prominent and visible veins in the abdomen and abdominal swelling. Learn about the symptoms of liver cirrhosis, causes and how the diagnosis is made.
What to do: The treatment for liver cirrhosis varies according to the cause, however it is important to maintain a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean meats and whole grains as they are easily digested. Understand how the treatment is done for cirrhosis.

5. Stones in the gallbladder
The stones in the gallbladder are formed due to the accumulation of calcium and cholesterol inside the gallbladder and cause, in addition to jaundice, fever above 38ºC, severe pain in the abdomen, back pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and loss of appetite. Find out what are the 7 leading causes of gallstone.
What to do: Treatment can be done with the use of medicines, surgery or from a proper diet rich in fruits, vegetables, salts and whole products. See what to eat in the gall bladder.
Sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell anemia is a type of hereditary anemia in which malformation of the red blood cells occurs which changes in shape, causing deficiency in the transport of oxygen to the body cells, which can cause jaundice, swelling and redness of the hands and feet, as well as pain in bones and joints. Understand the causes and how to control sickle cell anemia.
What to do: The treatment of sickle cell anemia is done according to the advice of the hematologist and usually involves the use of medicines and blood transfusions throughout life.
7. Thalassemia
Thalassemia is a hereditary genetic disease of the blood that causes yellow skin and eyes, symptoms such as tiredness, anemia, weakness and delayed growth.
What to do: Thalassemia does not have a cure, however the treatment is done according to the severity of the symptoms and is usually done with blood transfusions and use of folic acid supplements. See how treatment for thalassemia is done.

8. Anorexia nervosa
Anorexia nervosa is characterized by exaggerated and sudden loss of weight with distortion of body image, with anorexic individuals presenting with dry and yellow skin, as well as loss of hair or fine, brittle hair.
What to do: Treatment involves group, family, and behavioral therapy, in addition to nutritional monitoring, usually with the ingestion of dietary supplements to suppress nutritional deficiencies. Understand how the treatment for anorexia is done.
9. Excessive intake of beta-carotene
Beta-carotene is an antioxidant found in many foods and is primarily responsible for improving the immune system and helping to improve the tan. Thus, excessive consumption of foods rich in beta-carotene, such as carrots, papayas, pumpkin, tomatoes and broccoli, for example, can lead to the yellowish appearance of the skin. See what foods are rich in beta-carotene.
What to do: The best way to get the skin back to normal color is to reduce the consumption of these foods and seek other foods that have the same properties. Learn how color feeding can improve health.
10. Neonatal jaundice
Neonatal jaundice corresponds to the presence of yellowish skin in infants in the first days of life and is due to the accumulation of bilirubin in the bloodstream, which should be treated still in the hospital and preferably in the neonatal ICU. See how the Neonatal ICU works.
What to do: The treatment of jaundice in the baby is still in the hospital through phototherapy, which consists of exposing the baby to a light for a few days in order to lower the blood concentration of bilirubin. Understand what newborn jaundice is and how the treatment is done.
When to go to the doctor
It is important to go to the doctor as soon as the yellowish skin is noticed. In addition, it is important to keep an eye on other symptoms that may indicate problems in the liver, gallbladder, or pancreas, such as:
- Fever;
- Feces whitish or orange;
- Dark urine;
- Weakness;
- Excessive tiredness.
The hepatologist, gastroenterologist and endocrinologist are the most indicated doctors to guide the treatment of yellowed skin according to the cause, which can be done as a means of food re-education, medications or surgery.