The hidden spina bifida is a congenital malformation that develops in the baby in the first month of pregnancy and is characterized by incomplete closure of the spine. Usually it goes unnoticed, however, one of the symptoms is the growth of a tuft of hair on the back of the child.
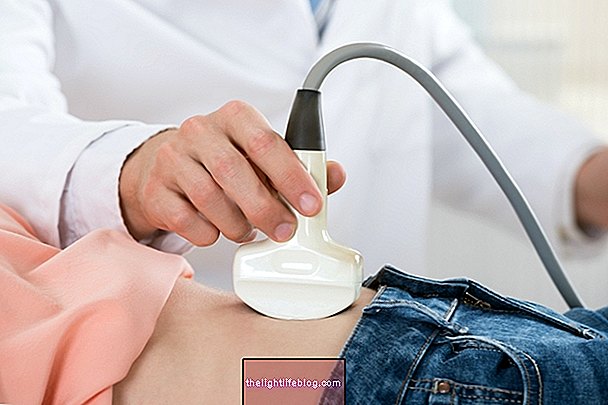
The spina bifida hidden in L5 or the spina bifida hidden in S1 are examples of the place in the spine where the spina bifida was formed. The diagnosis of occult spina bifida can be made through the ultrasound performed during pregnancy and an analysis of the amniotic fluid.
Photos of the hidden spina bifida


In general, the hidden spina bifida does not cause neurological problems in the child, since there is no involvement of the spinal cord and the meninges, which are the structures that protect it, therefore, no treatment of hidden spina bifida is necessary.
The causes of spina bifida occulta and cystic, which is another type of spina bifida, are unknown, but may arise due to insufficient intake of folic acid or alcohol consumption during pregnancy, for example.
Diagnosis of hidden spina bifida
The diagnosis of occult spina bifida can be made through ultrasonography performed during pregnancy and amniocentesis to evaluate the amount of alpha-fetoprotein in the amniotic fluid, which is very high in the case of spina bifida.
However, the hidden spina bifida can also be diagnosed after the baby's birth, by observing the hair growth in the lumbar region and being confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging. Here are the risks and the care you should take in: When to do MRI on the baby.
Symptoms of hidden spina bifida
Symptoms of hidden spina bifida include:
- Formation of a spot on the skin of the back;
- Formation of a tuft of hair on the back;
- Slight depression in the back, like a pit;
- Slight volume due to fat accumulation.
However, in most cases, the hidden spina bifida goes unnoticed.
Treatment for hidden spina bifida
Treatment for hidden spina bifida is usually not necessary because the child has no complications.
Useful links:
- Spina bifida
- Myelomeningocele