The treatment for fibrous dysplasia of the mandible, which consists of the growth of abnormal bone in the mouth, is recommended after the puberty period, ie after the age of 18, as it is during this period that the growth of the bone decreases and stabilizes, allowing that can be removed without re-growing.
However, if bone growth is very small and does not cause any change in the face or normal functions of the mouth, treatment may not be necessary, with only regular dental appointments being kept to assess the progress of the problem.
How is the treatment for fibrous dysplasia of the mandible
Normally, surgery is performed under general anesthesia in which the dental surgeon makes a small cut inside the mouth to reach the abnormal bone and remove the excess, giving symmetry to the face, which may have been altered after bone growth.
However, in the most severe cases, where the abnormal bone grows too fast and causes a very large face change or prevents activities such as chewing or swallowing, for example, the doctor may recommend anticipating surgery. In these cases it may be necessary to repeat the surgery if the bone grows again.
Recovery of surgery for fibrous dysplasia of the mandible
The recovery of surgery for fibrous dysplasia of the mandible takes about 2 weeks and during this time it is important to have some care such as:
- Avoid eating hard, acidic or hot foods for at least the first 3 days;
- Rest in bed for the first 48 hours;
- Avoid brushing your teeth in the first 24 hours, so you should only rinse your mouth;
- Do not wash the place of the surgery with toothbrush until the doctor's appointment, and the place with the antiseptic indicated by the doctor must be rinsed;
- Eat soft, creamy, and soft foods during the first week of recovery. Here's what you can eat in: What to eat when I can not chew.
- Sleep with one more pillow to keep your head elevated and avoid sleeping on the operated side;
- Do not lower your head for the first 5 days after surgery.
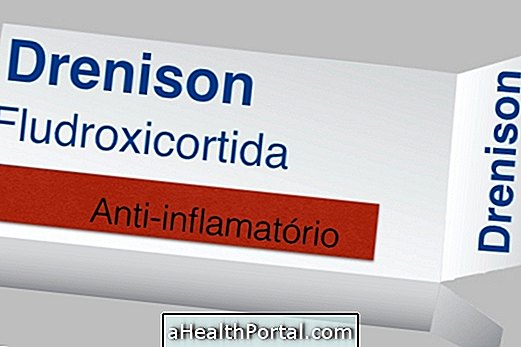
In addition to these care, the dentist may give other indications to avoid complications during surgery such as taking analgesic medicines such as Paracetamol and Ibuprofen, as well as antibiotics such as Amoxicillin or Ciprofloxacin, for example.
Symptoms of fibrous dysplasia of the mandible
The main symptom of fibrous dysplasia of the jaw consists of the abnormal growth of bone in a place of the mouth, that can cause asymmetry of the face and alteration of the body image. However, if the bone grows too quickly it can also lead to difficulty chewing, talking or swallowing.
Fibrous dysplasia of the mandible is more common in children around the age of 10 years, and if this is suspected, it is advisable to consult a pediatrician to make a CT scan and confirm the diagnosis by initiating appropriate treatment.