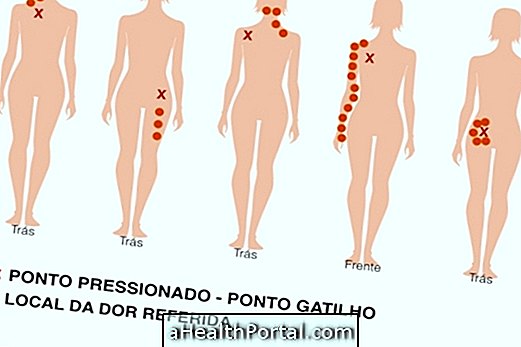
The treatment for osteoarthritis in the spine can be done by taking anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants and analgesics. Physical therapy sessions may also be indicated to relieve symptoms and prevent worsening of the disease, and as a last resort, perform surgery to remove the parts affected by arthrosis.
Treatment for arthrosis of the lumbar spine, which is the region of the lower back, should be performed under the guidance of an orthopaedist as soon as the first symptoms appear. The treatment for arthrosis in the cervical spine, which is the neck region, is very delicate and surgery is only performed in very serious cases.
Remedies for arthrosis in the spine
The medications for arthrosis in the spine depend on the stage the disease is in and the severity of the symptoms. The following options can be used:
- Analgesics and anti-inflammatories : help relieve pain and inflammation like paracetamol;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories : relieve pain and swelling such as ibuprofen and naproxen;
- Remedies that prevent deterioration of spinal wear : chondroitin and glucosamine;
- Anesthetic blocks or infiltrations with corticoids ;
- Application of analgesic and anti-inflammatory ointment : they are applied to reduce the pain in the place, like moment or voltaren.
It is important to note that the time, amount, and type of medicine best suited to treat osteoarthritis in the spine should be defined by the physician.
Physiotherapy for arthrosis in the spine
Physiotherapy for spinal arthrosis depends on the symptoms presented and the progression of the disease. The resources used by the physiotherapist include:
- Application of crushed ice wrapped in a wet towel on the spine : it should be done at an early stage and acute to relieve pain;
- Application of hot water bags in the spine : it can be used in a more advanced and chronic phase to relax the muscles and relieve the pain;
- Use of devices to relieve pain and inflammation : TENS, microcurrent, ultrasound, shortwave, laser;
- Manual therapy : it is done through stretches, pompings and joint mobilizations aiming to improve movements;
- Strengthening the muscles of the spine and legs : should be performed gradually, in a phase with few pains, to give more firmness to the joints and so that the symptoms do not get worse;
- Hydrotherapy and / or swimming : the exercises in the water brings many benefits because they relieve the symptoms and help to reduce the weight;
- Posture Correction : Techniques such as Global Posture Reeducation (RPG) and Pilates can be used to reduce spinal overload, improve alignment and strengthen muscles;
- Osteopathy : is a technique that must be performed by a specialized physiotherapist through manipulations of the spine in order to reduce the friction between the joints. Not all cases of spinal arthrosis can benefit from this technique.
Physiotherapy for spinal arthrosis should always be performed under the guidance of a physiotherapist. It can be performed in a physiotherapy clinic daily and at a later stage, when the symptoms are already more controlled, it should be done at least 3 times a week.
In addition to physical therapy and medication, the patient should adopt preventive measures so that the wear and tear of the spine does not worsen such as avoiding weight bearing, always maintaining a correct posture and remaining at rest whenever there is any pain or discomfort in the spine.
Surgery for arthrosis in the spine
Surgery for spinal arthrosis is only indicated in the last case, when the pain is incapacitating, when the neurological part is compromised and when all the existing treatments have been tried without success. The surgery options are:
- Fusion of the affected segments of the spine : a fixation of the vertebrae that cause the pain through the use of bone graft, rods or metallic screws is made. This will limit the movements of the affected site and decrease the pain;
- Artificial Disc Replacement : This is a more recent technique performed when there is a disc hernia associated with arthrosis. The disc is replaced by a metal prosthesis so that the joint maintains movement and reduces pain.
The patient with arthrosis in the spine should always try conventional treatments before proceeding to any type of surgery because not all of them have indications to operate the spine, and there are risks and complications such as nerve roots, nerve roots or bone marrow, risk of infections, and increased wear of the vertebrae that were not operated.