Zoonoses are diseases transmitted between animals and people and that can be caused by bacteria, parasites, fungi and viruses. Cats, dogs, ticks, birds, cows and rodents, for example, can serve as definitive or intermediate hosts for these infectious agents.
Zoonoses can be classified into:
- Anthropozoonosis, which are diseases of animals that can be transmitted to people;
- Zooantroponose, which are diseases of people but which can be transmitted to animals.
Zoonoses are considered a public health situation and, therefore, regional and state programs related to the prevention of these diseases are established. One of the measures is the control and care of domestic animals, encouraging regular visits to the veterinarian to carry out deworming and control of vaccines. In this way, it is possible to prevent animals from acquiring diseases and transmitting them to people.

Main zoonoses
There are several diseases transmitted between animals and people, however the most common are:
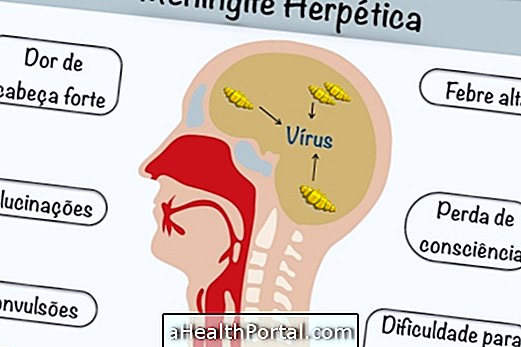
1. Anger
Human rabies is an infectious disease caused by the family virus Rhabdoviridae and it can be transmitted to people through the bite of an infected bat or dog, which is more likely to happen. Upon biting the person, the virus present in the animal's saliva enters the person's bloodstream directly and is able to spread to the nervous system, leading to the appearance of the characteristic signs and symptoms of the disease.
The first signs of human rabies can take 30 to 50 days after contact with the virus, depending on the person's immune system, and can be mistaken for a common infection. However, as the virus spreads into the bloodstream and reaches the nervous system, paralysis of the lower limbs, mental confusion, excessive agitation and increased production of saliva due to spasms of the throat muscle can occur. Know how to recognize the symptoms of anger.
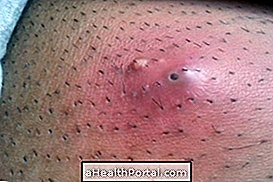
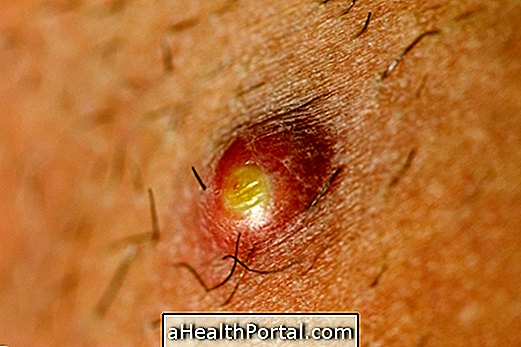
2. Sporotrichosis
Sporotrichosis in humans is a zoonosis transmitted through scratches and bites of cats infected by the fungus responsible for the disease, the Sporothrix schenckii, which can be found naturally in soil and plants. As cats are associated with most cases of sporotrichosis, this disease is popularly known as cat scratch disease, however domestic cats that have vaccination up to date are less at risk of being infected by this fungus and, consequently, of transmitting the disease.
The initial signs and symptoms of sporotrichosis appear about 7 to 30 days after contact with the fungus and the main indication of the infection is the appearance of a small, red and painful lump on the skin that grows over the days and forms pus. If the infection is not identified and treated, it is possible that the fungus will move to other parts of the body, mainly the lungs, resulting in respiratory symptoms. Learn more about sporotrichosis.
3. Brucellosis
Brucellosis is an infectious disease caused by bacteria of the genus Brucella and that it can be transmitted through contact with secretions, urine, blood or placental remains of infected cows. In addition, the transmission of the bacteria can happen through the ingestion of unpasteurized dairy products, such as milk and cheese, consumption of undercooked meat or during the cleaning of the stable or livestock movement, for example.
The symptoms of brucellosis appear days or months after infection, the initial symptoms being similar to those of the flu. However, as the disease progresses, more specific symptoms may appear, such as muscle pain, feeling unwell, abdominal pain, memory changes and tremors, for example.
4. Yellow Fever
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a virus whose life cycle occurs in mosquitoes, especially mosquitoes of the genus Aedes. Therefore, yellow fever is transmitted to people through the bite of infected mosquitoes. In forest regions, in addition to transmission by the mosquito of the genus Aedes, transmission of the virus by mosquitoes of the genus is possible Haemagogus and Sabethes and in these regions, monkeys are considered the main reservoirs of this virus.
The signs and symptoms of yellow fever appear between 3 and 7 days after the mosquito bite and the main ones are abdominal pain, headache and fever. The disease gets its name because the virus compromises the liver, interfering with the production of liver enzymes and clotting factors, increasing the amount of bilirubin in the blood and making the skin more yellow.
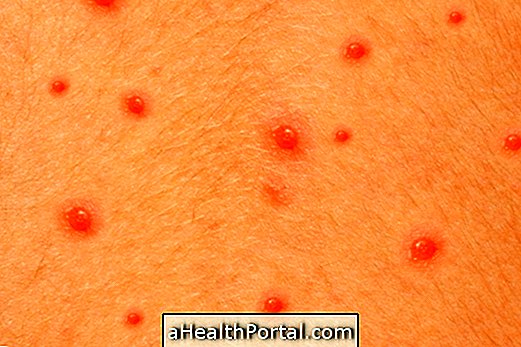
5. Dengue and Zika
Dengue and Zika are infectious diseases transmitted by viruses that have part of their life cycle in mosquitoes Aedes aegypti, which bites people, transmits the virus, which completes its life cycle in the person's body and leads to the appearance of signs and symptoms of the disease.
Despite dengue and Zika without being caused by different viruses, dengue virus and Zika virus respectively, have similar symptoms, with pain in the body and head, tiredness, fever, joint pain and the appearance of red spots on the skin. In the case of Zika virus infection, itching and redness and increased sensitivity in the eyes can also be seen.

6. Leishmaniasis
Like yellow fever, leishmaniasis is also transmitted by the bite of a mosquito, which in this case is the mosquito of the genus Lutzomyia, popularly known as straw mosquito. The infectious agent responsible for the disease is the protozoan of the genus Leishmania, being most frequently found in Brazil the speciesLeishmania braziliensis, Leishmania donovani and Leishmania chagasi.
After the mosquito bite, the protozoan enters the person's body and leads to the development of symptoms whose severity can vary according to the person's species and immune system. There are three main types of leishmaniasis:
- Cutaneous leishmaniasis, which is characterized by the appearance of one or more lumps at the site of the mosquito bite and which in some days can develop into an open and painless wound;
- Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis, in which the lesions are more extensive and there is involvement of the mucosa, mainly of the nose, pharynx and mouth, which may cause difficulty in speaking, swallowing or breathing;
- Visceral leishmaniasis, whose symptoms evolve in a chronic way and there may be an enlarged liver and spleen, weight loss and increased risk of other infections.
As the symptoms can be quite compromising and make the person's life rich, it is important that as soon as the first indicative signs of leishmaniasis appear, the person goes to the hospital to make the diagnosis and start treatment, preventing complications.
7. Leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is a disease caused by the bacteria Leptospira, which can be found in rats, mainly. Transmission to people occurs through contact with the urine or feces of the contaminated animal, with the entry of bacteria into the person's body through mucous membranes or skin wounds and resulting in symptoms such as fever, chills, red eyes, headache. head and nausea.
Situations of floods, puddles and places where there is a lot of garbage accumulation are considered to be at high risk of contamination by Leptospira, because in these situations the urine of infected animals can spread more easily, with a greater risk of infection.
8. Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease popularly known as cat disease, because the parasite responsible for this disease, the Toxoplasma gondii, has as its intermediate host felines, especially cats, that is, part of its life cycle must be in the cat. That way, people can be infected by Toxoplasma gondii through direct contact with feces of infected cats or through ingestion of water or food contaminated with cysts of the parasite.
In most cases, toxoplasmosis is asymptomatic, however it is essential that pregnant women perform serological tests to identify the parasite, because if the woman has toxoplasmosis, it can transmit to her child during pregnancy, which can result in complications for the drink.
9. Cutaneous larva migrans
Cutaneous larva migrans, popularly known as the geographic bug, is an infectious disease caused by parasites Ancylostoma brasiliense and Ancylostoma caninum, which can be found in dogs and cats. These parasites are eliminated in the feces of animals and when the person walks barefoot, for example, they can enter the organism through small wounds present at the site, leading to the appearance of symptoms such as itching and local redness, in addition to being able to perceive a little path rectilinear in the skin, which is indicative of the parasite's displacement.
To avoid infection, it is recommended that pets be taken to the veterinarian periodically so that vaccines are updated and deworming is carried out. In addition, it is recommended to avoid walking barefoot in environments that may contain feces from dogs and cats to decrease the risk of infection.
See how to know if you are a geographic animal.

10. Teniasis
Teniasis is a zoonosis caused by the parasite Taenia sp. which is transmitted to people by eating raw or undercooked pork or beef. This parasite is popularly known as solitary, as it reaches large dimensions, attaches itself to the intestinal wall and hinders the absorption of nutrients, leading to the appearance of symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea and weight loss, for example.
The person infected with Taenia sp. releases in its feces eggs of this parasite, which can contaminate other people and animals, starting another life cycle. Understand how the life cycle of the Taenia sp.
11. Lyme disease
Lyme disease is one of the diseases that can be transmitted by ticks, which can be found in cats and dogs, mainly. This disease is transmitted by the tick of the genusIxodes infected by the bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi, which when the person bites releases the bacteria and causes a local reaction that can be perceived through swelling and redness in the area.
If the disease is not identified and treated, the bacteria can spread through the bloodstream and reach several organs, which can compromise the nervous and cardiac systems. Therefore, it is important that the tick is removed from the skin immediately and antibiotic treatment is started shortly thereafter.
Learn about other tick-borne diseases.
12. Cryptococcosis
Cryptococcosis is popularly known as pigeon disease, because the fungus responsible for the infection, the Cryptococcus neoformans, performs part of its life cycle in these animals, being released in the feces. In addition to being present in pigeons, this fungus can also be found in soil, trees and cereals.
The transmission of cryptococcosis occurs through the inhalation of spores or yeasts of this fungus present in the environment, which can lead to the development of respiratory symptoms, such as sneezing, runny nose and difficulty breathing. However, if the infection is not identified and treated, it is possible that the fungus will spread and lead to more severe symptoms, such as chest pain, stiff neck and mental confusion, for example. See more symptoms of cryptococcosis.
O Cryptococcus neoformans it is considered an opportunistic fungus, in other words, normally the symptoms are only developed in people who have compromised immune system, as in the case of people who are carriers of the HIV virus or who are being treated for cancer.

How Zoonoses are transmitted
All animals can transmit diseases. Thus, transmission can happen in several ways, such as:
- Animal bite or scratch;
- Insect bite;
- Contact with objects or excreta of infected animals;
- Ingestion of water or food contaminated by feces, urine or saliva of an infected animal.
People who work or who have frequent contact with animals are more likely to acquire a zoonosis, so it is important to pay attention to hygiene habits both personal and animal so as not to run the risk of acquiring a disease. In the case of people who work with animals, it is recommended that protective equipment be used at the time of contact with the animal, such as gloves and masks, mainly, to avoid contamination.
If the person suspects that he or she has a disease that may have been transmitted by animals, it is recommended to go to the doctor to have tests done and to start the appropriate treatment.
How to avoid
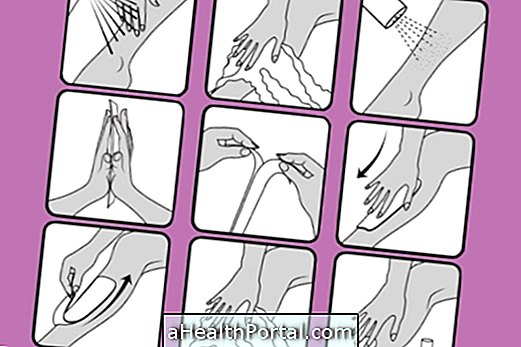
To avoid zoonoses, it is important to pay attention to the hygiene of the environment and personal hygiene, washing your hands always after coming into contact with the animals and keeping the places inhabited by the animals in ideal conditions. In addition, it is important to keep the animals' vaccines up to date.
Ticks, cockroaches and ants can also transmit diseases, so it is important to keep the house clean and the animals dewormed. At the time of pest control, if the person has a pet, it is recommended to isolate the animal in another room for a few hours so that it is not intoxicated by the product used.
In the case of mosquitoes, for example, mosquito control campaigns are periodically launched by the government, demonstrating actions that may have been taken to prevent the proliferation of mosquitoes and, consequently, the spread of diseases. See in the following video how to prevent mosquito-borne diseases:

It is also recommended to be careful when handling and preparing food, paying attention to water quality and avoiding contact with unknown animals. In addition, it is important that the government promote strategies for sanitary control, hygiene and vaccination in animal husbandry facilities. See more on how to prevent infectious diseases.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
Bibliography
- RIO DE JANEIRO'S CITY HALL. Zoonoses. Available in: . Accessed on Aug 28, 2019
- MINISTRY OF HEALTH. Manual of Surveillance, Prevention and Control of Zoonoses. 2016. Available at:. Accessed on Aug 28, 2019
- GOVERNMENT OF THE STATE OF ESPÍRITO SANTO. Yellow fever. Available in: . Accessed on 29 Aug 2019