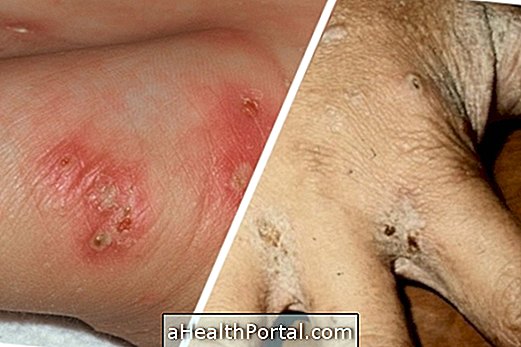
Collagenosis, also known as collagen disease, is characterized by a group of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases that harm the connective tissue of the body, which is the tissue formed by fibers, such as collagen, and is responsible for functions such as filling the spaces between organs, provide support, in addition to helping in the defense of the body.
The changes caused by collagenosis can affect various organs and systems of the body, such as skin, lungs, blood vessels and lymphatic tissues, for example, and produce mainly dermatological and rheumatological signs and symptoms, which include joint pain, skin lesions, skin changes, blood circulation or dry mouth and eyes.
Some of the main collagenoses are diseases such as:
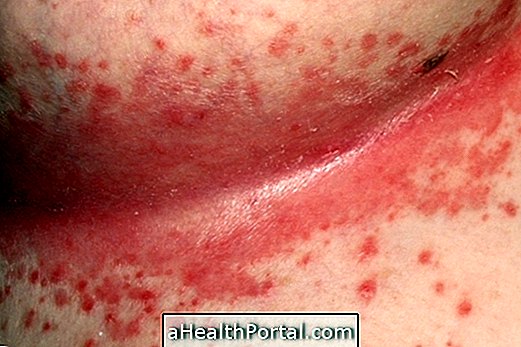
1. Lupus

It is the main autoimmune disease, which causes damage to organs and cells due to the action of autoantibodies, and is more common in young women, although it can occur in anyone. Its cause is not yet completely known, and this disease usually develops slowly and continuously, with symptoms that can be mild to severe, which varies from person to person.
Signs and symptoms: Lupus can cause a wide variety of clinical manifestations, from localized to disseminated throughout the body, including skin blemishes, oral ulcers, arthritis, kidney changes, blood disorders, inflammation of the lungs and heart.
Learn more about what it is and how to identify lupus.
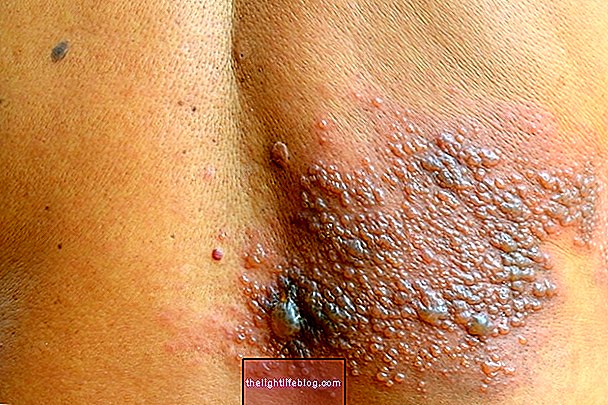
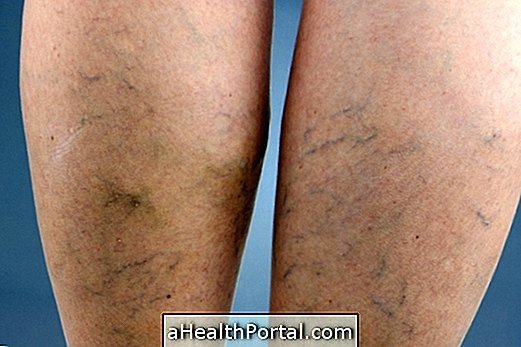
2. Scleroderma

It is a disease that causes the accumulation of collagen fibers in the body, the cause of which is still unknown, and mainly affects the skin and joints, and can also affect the circulation of blood and other internal organs, such as the lungs, heart, kidneys and gastrointestinal tract.
Signs and symptoms: there is usually thickening of the skin, which becomes more rigid, shiny and with circulatory difficulties, which worsens slowly and continuously. When it reaches internal organs, in its diffuse type, it can cause breathing difficulties, digestive changes, in addition to impaired heart and kidney functions, for example.
Better understand the symptoms of the main types of scleroderma and how to treat it.
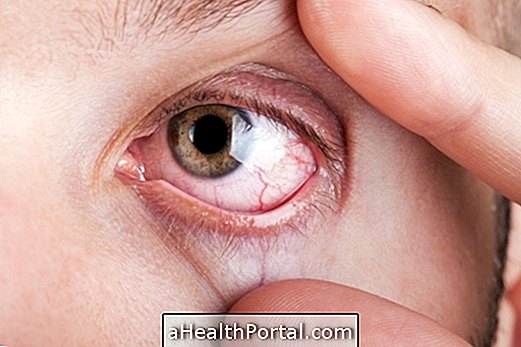
3. Sjogren's syndrome

It is another type of autoimmune disease, characterized by the infiltration of defense cells into glands in the body, hindering the production of secretion by the lacrimal and salivary glands. This disease is more common in middle-aged women, but it can occur in anyone, and can appear in isolation or accompanied by diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, scleroderma, vasculitis or hepatitis, for example.
Signs and symptoms: dry mouth and eyes are the main symptoms, which can worsen slowly and progressively, causing redness, burning and a feeling of sand in the eyes or difficulty swallowing, speaking, increased tooth decay and burning sensation in the mouth . Symptoms in other parts of the body are more rare, but can include tiredness, fever and joint and muscle pain, for example.
Better understand how to identify and diagnose Sjogren's syndrome.
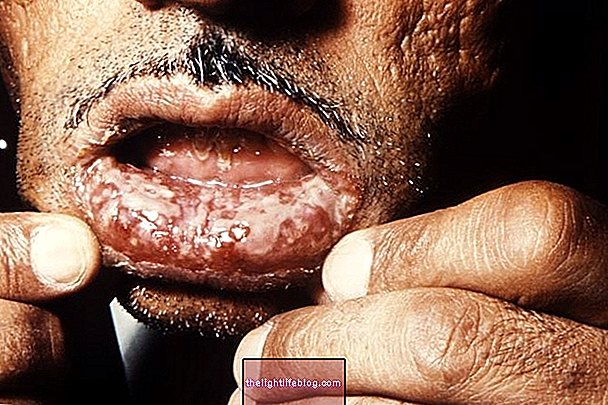
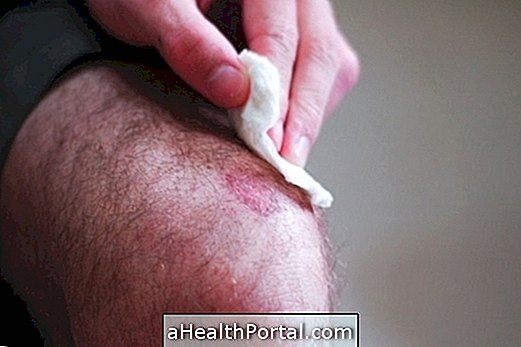
4. Dermatomyositis

It is also a type of autoimmune disease that attacks and compromises muscles and skin. When it affects only the muscles, it can also be known as polymyositis. Its cause is unknown, and it can arise in people of all ages.
Signs and symptoms: it is common to have muscle weakness, more common in the trunk, hindering movements of the arms and pelvis, such as combing the hair or sitting / standing up. However, any muscle can be reached, causing difficulties in swallowing, moving the neck, walking or breathing, for example. Skin lesions include reddish or purplish spots and flaking that can get worse with the sun.
Find out more details on how to identify and treat dermatomyositis.
How to confirm the diagnosis
To diagnose collagenosis, in addition to clinical evaluation, the doctor may order blood tests that identify the inflammation and antibodies present in these diseases, such as FAN, Mi-2, SRP, Jo-1, Ro / SS-A or La / SS- B, for example. Biopsies or analysis of inflamed tissues may also be necessary.
How to treat collagenosis
The treatment of a collagen disease, as well as any autoimmune disease, depends on its type and severity, and should be guided by a rheumatologist or dermatologist. Generally, it involves the use of corticosteroids, such as Prednisone or Prednisolone, in addition to other more potent immunosuppressants or immunity regulators, such as Azathioprine, Methotrexate, Cyclosporine or Rituximab, for example, as a way of controlling immunity and decreasing its effects on the body.
In addition, some measures such as sun protection to prevent skin lesions, and artificial eye drops or saliva to reduce dryness of the eyes and mouth, may be alternatives to reduce symptoms.
Collagenosis has no cure, however science has sought to develop more modern therapies, based on immunity control with immunotherapy, so that these diseases can be controlled more effectively.
Why it happens
There is still no clear cause for the emergence of the group of autoimmune diseases that cause collagenosis. Although they are related to the wrong and excessive activation of the immune system, it is not known exactly what causes this situation.
It is very likely that there are genetic and even environmental mechanisms, such as lifestyle and eating habits, as the cause of these diseases, however, science still needs to better determine these suspicions through further studies.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther