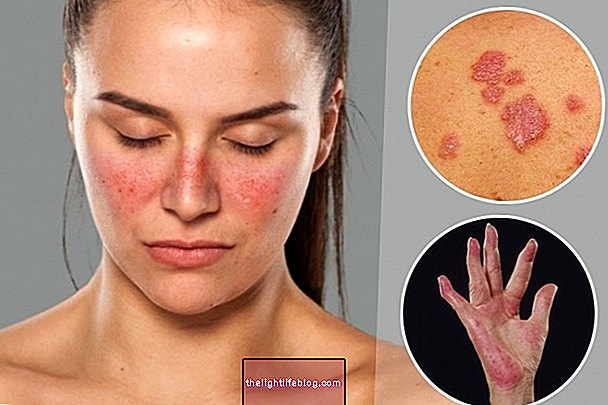
The treatment for scleroderma is to reduce the symptoms of patients and therefore may include the use of:
- Anti-fibrotic medications, such as Penicillamine, that decrease collagen build-up;
- Vasoactive drugs, such as Nifedipine, Diltiazem, or Pentoxifylline, which dilate the veins;
- Remedies for high blood pressure, such as Captopril, to prevent cardiovascular problems;
- Immunosuppressive medicines, such as Cyclophosphamide or Azathioprine, used for lung problems;
- Stomach medicines, such as Cisapride or Omeprazole, to prevent problems in the esophagus, such as esophagitis;
- Anti-inflammatory medicines, such as Ibuprofen or Ketoprofen, to decrease joint pain.
These remedies are more common in the treatment for systemic scleroderma, however they can also be used in localized scleroderma.
In addition to the remedies, patients, during treatment, should sleep with the headboard elevated, keep their hands and feet warm, do regular exercise and go to physical therapy.
Another treatment that may be useful to treat this disease is phototherapy, which consists of exposing the affected area to a special light in clinics or hospitals. Learn more details of this treatment by clicking here.
Physiotherapeutic treatment for scleroderma
Physiotherapeutic treatment for scleroderma is especially used in the treatment of localized scleroderma and serves to decrease pain, prevent joint contractures and maintain limb function and amplitude.
For this, the physical therapy treatment for scleroderma consists of exercises of mobilization and manipulation that must be done daily or according to the indication of the physiotherapist.
Useful links:
- Scleroderma
- Symptoms of scleroderma