Generally, the woman can get pregnant even if she has a fibroid, and this does not usually bring risks to the mother or the baby. However, when a woman becomes pregnant with a myoma, it can cause bleeding, due to hormonal changes typical of pregnancy, which can cause enlargement of the myoma.
Symptoms in pregnancy arise only when there are large, numerous fibroids or in the inner part of the uterus, and this may even become a risky pregnancy. The main treatment done is rest and use and analgesic medications such as paracetamol and ibuprofen.
Risks of myoma in pregnancy
Myoma in pregnancy is not usually severe, but complications may occur in women who have a large myoma, especially if it is located in the inside of the uterus, such as intramural myoma. The risks can be:
- Abdominal pain and colic, which may appear at any time during gestation;
- Abortion, happens in the first trimester of pregnancy, because some fibroids can cause intense bleeding;
- Placental abruption, in cases of fibroids that occupy the site or make it difficult to attach the placenta to the wall of the uterus;
- Limitation of growth of the baby, by very large fibroids that occupy or push the uterus;
- Preterm delivery, because delivery can be anticipated in large fibroids, which cause bleeding and cramping.
The few cases in which these situations occur are more delicate and should be very well followed up by the obstetrician, with more frequent consultations and more examinations, such as ultrasonography.

How is the treatment done?
It is not always necessary to treat myoma in pregnancy, but in any case, rest and use of analgesic drugs, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, is indicated in women who have symptoms of pain and mild bleeding.
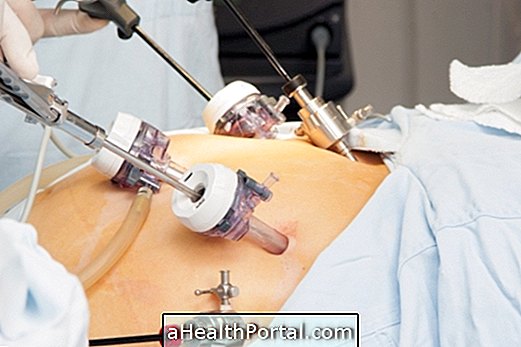
Surgery for myoma removal may be indicated during pregnancy, and may be done by the belly or vagina. It is usually indicated in cases of fibroids that cause pain and persistent bleeding or that are large enough to cause risks to the baby or woman. But even in these cases, the decision to perform the surgery should be made when the risk of surgery is less than the risk of the fibroid remaining inside the uterus.
Understand the signs and symptoms of myoma, and how they can be treated.
How is delivery?
Since most cases are safe for the mother or baby, birth may be normal, especially in women with small fibroids who have few symptoms. A cesarean section can be indicated by the obstetrician in cases of pregnant women with fibroids who:
- They bleed or are at risk of bleeding, causing a greater chance of hemorrhage at delivery;
- They are very painful, causing pain and suffering to the woman during childbirth;
- They take up a lot of space in the uterus, making it difficult for the baby to leave;
- They involve a large part of the wall of the uterus, making it difficult or altering its contraction.
The choice of delivery type can be discussed personally with the obstetrician, taking into account the size and location of myoma, as well as the woman's desire to have a normal delivery or cesarean delivery.
One advantage of having a cesarean section is the possibility of removing the fibroid during labor, especially if it is outside the uterus.