Treatment for pubalgia, which is a chronic problem that affects many athletes, such as soccer players, runners or hockey players, should be guided by an orthopedist and is usually done with resting and applying ice packs to the groin during 7 to 10 days.
In addition, in these early days, the doctor may also prescribe the ingestion of anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Ibuprofen or Diclofenac, to relieve pain and reduce swelling of the affected region.
After 2 weeks, physiotherapy should be started and, in more severe cases, surgery may be needed to treat pubalgia.
Physiotherapy for pubalgia
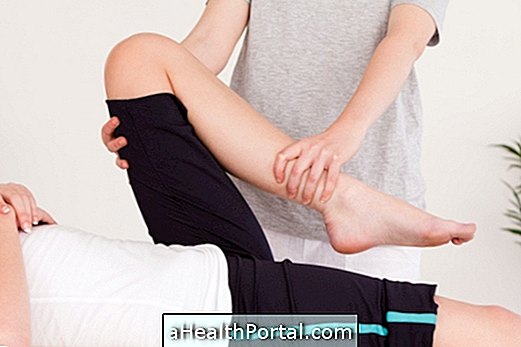
Physiotherapy treatment for pubalgia should only be started promptly and lasts for about 6 to 8 weeks when the pain started shortly but can take from 3 to 9 months when the pain has arisen for a long time.
Usually, during physical therapy sessions for pubalgia, the patient performs exercises that help strengthen the muscles of the abdomen and thigh, making treatment faster. Check how the treatment is done in physical therapy.
Surgery for pubalgia
The surgery for pubalgia is used only in the most severe cases, when the problem is not only treated with the use of physiotherapy. In these cases, the orthopedist performs a surgery to make the muscles of the region stronger, avoiding the appearance of new inguinal hernias.
After surgery for pubalgia, the doctor will guide the patient to a recovery plan so that he can return to sports activities in about 6 to 12 weeks.
Alternative treatment for pubalgia
The natural treatment for pubalgia should only be used as a supplement to medical treatment, it can be done with acupuncture to relieve pain and homeopathic remedies, such as Homeofaln, to reduce swelling, for example.
Signs of pubertal improvement
Signs of pubertal amelioration may take up to 1 month to appear and include pain relief, reduction of swelling in the groin, and ease of movement of the leg on the affected side.
Signs of worsening of pubalgia
Signs of worsening occur mainly in athletes who have had a serious injury that has caused pubalgia and usually include increased pain and swelling, as well as difficulty walking or small leg movements.