Cervical dysplasia occurs when there is a change in the cells located inside the uterus, which may be benign or malignant, depending on the type of cells with changes that are found. This disease usually does not cause symptoms and does not progress to cancer, ending in most cases by healing alone.
This disease can arise due to several factors, such as early intimate contact, multiple sexual partners or infection by sexually transmitted diseases, especially HPV.

How is the treatment done?
Cervical dysplasia is a disease that in the vast majority of cases heals itself. However, it is important to regularly follow the evolution of the disease, in order to diagnose early complications that may require treatment.
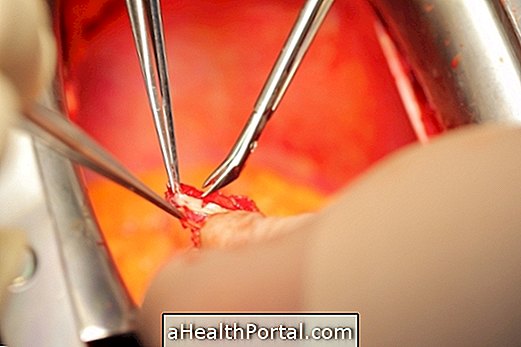
Only in the most severe cases of severe cervical dysplasia may the treatment be required, which should be guided by a gynecologist. In some of these cases, the doctor may indicate performing surgery to remove the affected cells and prevent the development of cancer.
How to prevent cervical dysplasia
To avoid cervical dysplasia, it is important for a woman to protect herself against sexually transmitted diseases, especially HPV, so she should:
- Avoid having multiple sexual partners;
- Always use a condom during intimate contact;
- Do not smoke.
Learn all about this disease by watching our video:

In addition to these measures, the woman can also be vaccinated against HPV until the age of 45, thereby reducing the chances of developing cervical dysplasia.