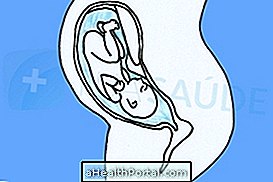
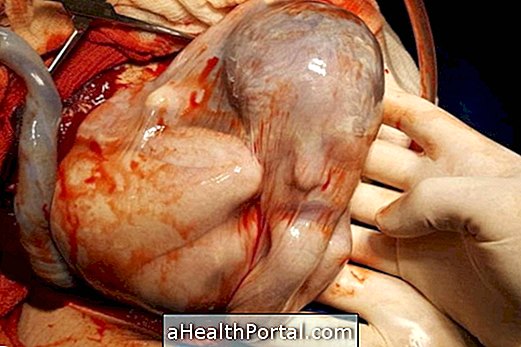
Empathic delivery occurs when the baby is born into the intact amniotic sac, ie when the pouch does not burst and the baby is born into the sac with the entire amniotic fluid.
Although it is very rare, this type of delivery is more common in cesarean delivery, but it can also happen in normal delivery when the baby is premature because the size of the amniotic sac is smaller and so the baby and the pouch pass easily through the canal vaginal age with a lower chance of rupturing before or during labor, as it happens naturally in the vast majority of cases.
Emptorized childbirth poses no risk to the baby or mother, and in many cases may even help protect the baby from any infection the mother may experience.
Advantages of an empathic birth
The empelicated birth does not present risks for the baby, nor for the mother, however it can bring advantages such as:
- Protecting the Premature Baby: When the baby is premature, the amniotic sac can help protect against birth trauma, avoiding fractures or bruising;
- Avoid HIV transmission: in the case of HIV positive mothers, this type of delivery avoids contact with blood during birth, reducing the chances of transmission of the disease.
Although it may bring some advantages to the baby, this type of delivery is difficult to program, happening almost always, spontaneously and naturally.
What happens after delivery

While the baby is inside the amniotic sac continues to receive all nutrients and oxygen through the umbilical cord, there being no risk for its survival. However, it needs to be removed from the bag so the doctor can assess whether you are healthy.
Unlike normal birth, where the baby passes through the birth canal is "squeezed" and the amniotic fluid, which the baby ingested and aspirated during gestation, comes out naturally allowing the baby to breathe, in which case the doctor uses a thin tube to aspirate the liquid from inside the baby's nose and lungs, as in a cesarean section.
Then, when the baby leaves, the doctor makes a small incision in the amniotic pouch to remove it and allow it to breathe normally.
How to schedule this type of delivery
This type of delivery is difficult to program, occurring in most cases, naturally in 1 in 80 thousand deliveries. However, when a pregnant woman is HIV positive, the doctor can schedule a cesarean section to withdraw the baby before the age of 38 weeks, and during labor, try to remove the baby without rupturing the amniotic sac so there is less possible contact with the infected blood of the mother.
Learn more about what a woman who is infected with AIDS should deliver to protect her baby.