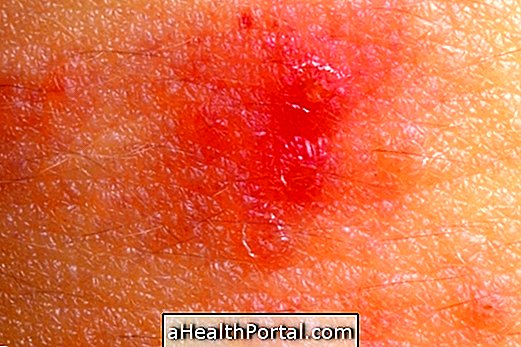
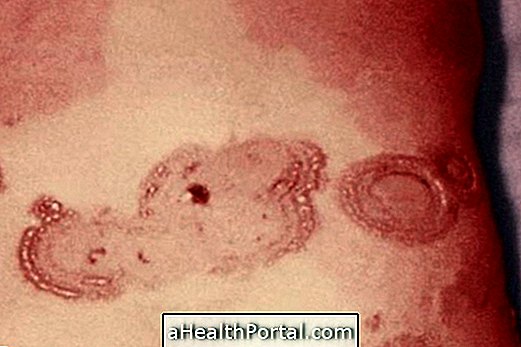
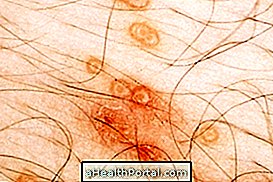
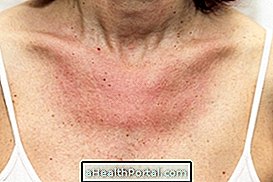
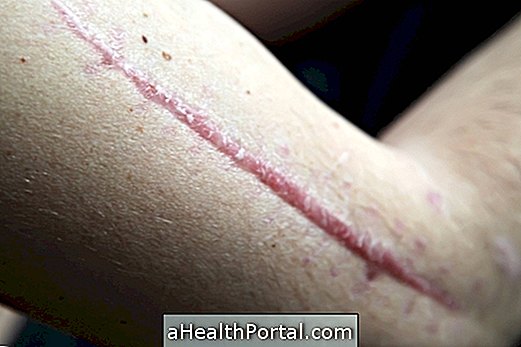
Actinic keratosis is a skin disease that causes the appearance of an irregularly scaly lesion, especially in regions of the skin that are very exposed to the sun like the apples of the face, forehead, lips, ears, arms or hands.
Although keratosis can develop over a number of years, it usually develops symptoms only after the age of 40 and is usually not accompanied by any other signs.
Most cases have healing and are benign and therefore the treatment is only done to improve the appearance of the skin. However, there are also cases where keratosis can become skin cancer, and it is recommended that all cases be evaluated by a dermatologist as early as possible, even if there is no history of skin cancer in the family.
Main symptoms
The symptoms of actinic keratosis are:
- Irregular and scaly lesions on the skin, less than 2.5 cm;
- Injury with hard surface;
- Itching and increased sensitivity in the skin;
- Pain or burning sensation in the affected region.
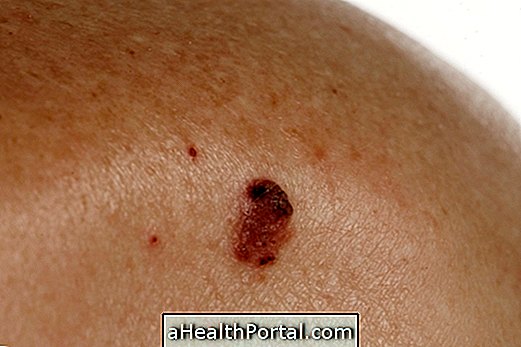
The lesions of actinic keratosis can range from reddish, darkened, hard, scaly, lofty or rough. Actinic keratosis affects a greater proportion of people with fair skin, since they have less pigmentation, facilitating their identification.
This change is only caused by solar UV rays, so the only way to avoid it is to use a sunscreen daily in areas exposed to the sun and avoid going in tanning salons.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment for actinic keratosis should always be directed by a dermatologist, since it is necessary to evaluate the lesions to know if there is a risk of becoming cancer. However, in most cases, the doctor recommends taking the treatment not only to improve the appearance of the skin, but also to prevent it from turning cancer with sun exposure.
Thus, there are different forms of treatment that include:
- Use of creams, with Fluorouracil or Imiquimod: are creams that work as chemo or that strengthen the immune system, facilitating the elimination of the cells that cause the injury;
- Cryotherapy : allows to freeze and eliminate cells from actinic keratosis lesions, over some sessions;
- Phototherapy : A beam of light is used to remove superficial cells from the lesion;
- Chemical Peeling : An acid is applied over the lesion to remove layers of damaged skin.
These treatments are selected by the doctor according to the degree of development of the lesions and the skin type of each person. Although some treatments may eliminate some people's injuries from time to time, they may not have the same result in others, and it is important to adapt the treatment over time.
In addition, there are also cases of actinic keratosis lesions that reappear some time after treatment, especially if sunscreen is not used every day.