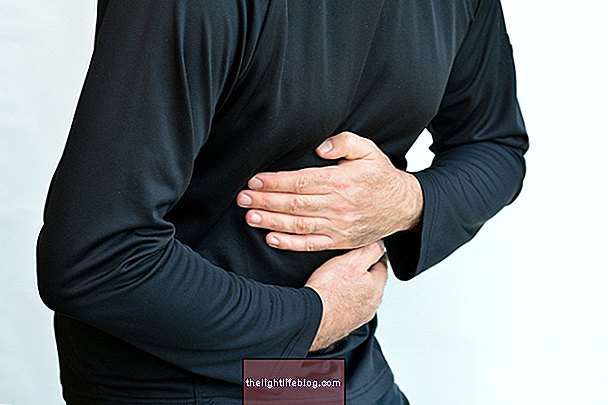
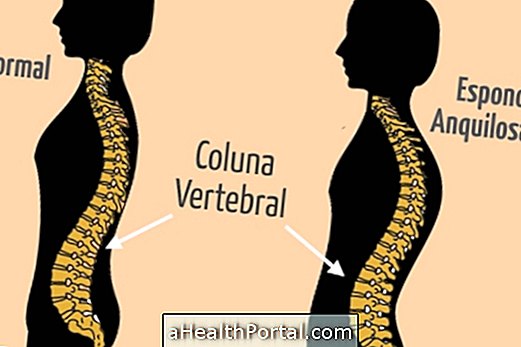
Ankylosing Spondylitis especially affects the articulations of the spine, as it is a chronic inflammatory disease where there is a tendency for these joints to unite between them, which causes symptoms such as pain, loss of mobility and less flexibility in the spine
This disease is more common in men between 20 and 30 years of age, being less common in women. It is a genetic disease that can lead to disability, being in some cases associated with other problems such as inflammatory bowel diseases or psoriasis, for example.
Main Symptoms
Some of the main symptoms caused by this disease include:
- Pain in the gluteal region and deep in the back, which does not pass when you are at rest;
- Sensation of stiffness or movements trapped in the region of the spine and neck, especially in the morning upon waking;
- Joint pain;
- Fever and fatigue;
- Loss of appetite;
- Pain and inflammation of the ligaments or tendons;
- Inflammation of the Achilles tendon that causes pain in the heel;
- Difficulty breathing.
Outbreaks of inflammation can also occur in places other than the spine, which can arise in other joints such as shoulders, hips, knees and ankles, causing pain and discomfort due to inflammation. In addition to the aforementioned symptoms, the appearance of an inflammation in the eye called uveitis, which causes pain and redness in the eyes, is also common, and how much untreated it can lead to blindness. See your symptoms and treatment here.
The pain that this disease causes is usually slow and gradual, and often it is not possible to identify when the first symptoms of the disease began to appear. This is usually worse in the last hours of the day and soon in the morning, improving with daily activities and exercise.
Main causes
The causes that lead to the appearance of Ankylosing Spondylitis are not known, however it has been identified that this disease is related to the presence of a specific antigen in the body called HLA-B27.
This antigen passes genetically among members of certain families, triggering an abnormal response in the body and causing the disease.
How Diagnosis Is Made
The diagnosis of this disease is made through the observation and evaluation of the physical symptoms manifested, where the doctor evaluates the characteristics of the pain and if there is any sensation of rigidity or movements trapped in the region of the spine and neck.
Confirmation of the diagnosis can be made by performing radiographs to the basin and spine to identify changes in joints and vertebrae. In addition, in cases where the X-ray identifies changes, the physician may also request a genetic test to identify the presence of the HLA-B27 antigen.
Ankylosing Spondylitis although it has no cure, can be treated with analgesics, anti-inflammatories and physiotherapy, and in some cases surgery may be necessary. Learn more about how this disease is treated by clicking here.