Oral leukoplakia is a condition in which small white plaques grow on the tongue and sometimes inside the cheeks or gums, for example. These stains do not cause pain, burning or itching, and usually go away without needing treatment.
The main cause of this condition is the frequent use of cigarettes, but it can also be caused by the use of irritating substances, such as frequent ingestion of alcoholic beverages, for example.
Although most often it is a benign condition, in some people it may be a sign of an Epstein-Barr virus infection, and is called hairy leukoplakia. Infection with this virus is most common when the immune system is weakened by some disease, such as AIDS or cancer, so it is important to consult a general practitioner to identify if there is any disease that needs to be treated.
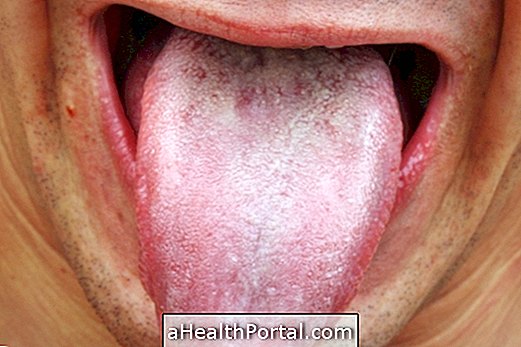
Main symptoms
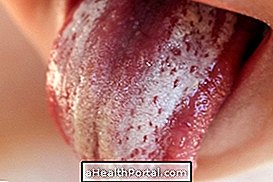
The main symptom of leukoplakia is the appearance of blemishes or plaques in the mouth, with the following characteristics:
- White-gray color;
- Stains that can not be removed by brushing;
- Irregular or smooth texture;
- They rarely cause pain or discomfort.
In the case of hairy leukoplakia, it is also common for the plaques to appear to have small hairs or folds, developing mainly on the sides of the tongue.
Another rare symptom is the appearance of small red dots over white patches, which usually indicate cancer, but need to be evaluated by a doctor to confirm the suspicion.
How is the diagnosis made?
In most of the chaos the diagnosis is made by the doctor only with the observation of the spots and evaluation of the clinical history of the person. However, if there is suspicion that leukoplakia may be caused by a disease, the doctor may order some tests such as spot biopsy, blood tests, and even a CT scan.
What can cause leukoplakia
The specific cause of this condition is not yet fully understood, however, chronic irritation of the lining of the mouth, mainly caused by the use of cigarettes, seems to be its main cause. Other factors that can also cause this type of inflammation are:
- Consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- Use of chewing tobacco;
- Broken teeth that brush against the cheek;
- Use of improperly sized or improperly sized dentures.
Although it is more rare, there is still the hairy leukoplakia that is caused by infection of the Epstein-Barr virus. The presence of this virus in the body is relatively common, however, it is kept dormant by the immune system, causing no symptoms. However, when the immune system is weakened by a disease, such as AIDS or cancer, symptoms can develop and leukoplakia develops.
How is the treatment done?
In most cases, leukoplakia stains do not need treatment, disappearing over time without causing any health problems. However, when being triggered by cigarette or alcohol use, for example, it may be advisable to decrease its use. Already when they are caused by broken teeth or badly adapted dentures, it is advised to go to the dentist to treat these problems.
Already in the case of suspected mouth cancer, the doctor may recommend the removal of the cells affected by the spots, through a minor surgery or less invasive treatments, such as cryotherapy. In these cases, it is also important to have regular consultations to see if blemishes recur or other cancer symptoms appear.
The treatment of hairy leukoplakia is usually done with the treatment of its cause, since the spots do not increase the risk of cancer, nor cause health problems. Understand how treatment for AIDS is done, one of the main causes of hairy leukoplakia.