Cigarette smoking can cause almost 50 different diseases, and this is due to the large amount of chemicals in its composition, which have bad health consequences and are responsible for causing cancer in various organs, lung diseases such as bronchitis and emphysema, and diseases such as high blood pressure, stroke, and stroke.
Even people who smoke little or people who do not smoke, but inhale the smoke of others, may suffer from a disease related to this habit, as the toxic substances of cigarette smoke have a high capacity to cause inflammation and changes in the genetics of cells.

In addition, not only the traditional industrialized cigarette makes bad, but also the versions chewed tobacco, straw, pipe, cigar and narghile.
1. Pulmonary emphysema and bronchitis
Emphysema and bronchitis, known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, arise because cigarette smoke causes inflammation in the tissue lining the airways, leading to permanent damage and reducing lung capacity to effect gas exchange efficient.
The main symptoms that arise in this type of disease are shortness of breath, chronic cough and cases of frequent pneumonia. Shortness of breath initially arises when exerting effort, but as the disease worsens, it may arise even when standing still. Understand how to identify and treat COPD.
2. Infarction and stroke
Cigarette smoking causes inflammation in the wall of blood vessels, thus increasing the chances of developing cardiovascular disease such as heart attack, stroke, thrombosis and aneurysms.
The person who smokes may be more likely to have high blood pressure, have chest pains such as angina, and have plaques of fats in the vessels, for example, which increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, especially if associated with other risk situations, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol and diabetes.
3. Sexual impotence
Smoking causes impotence in men both by altering the release of hormones important for intimate contact, and by inhibiting the blood flow that pumps blood into the muscle that maintains the erection.
Thus, the person who smokes may have difficulty initiating or maintaining intimate contact until the end, causing some constraints, however, stopping smoking usually partially or totally reverses this situation.

4. Rheumatic diseases
Not only does smoking increase the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis, with pain, swelling and redness in the joints, especially in the hands, but they also increase the severity and difficulty of your treatment.
Other rheumatic and autoimmune diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis and lupus, for example, are also more likely to develop in people who smoke due to increased inflammation and dysfunction of the body's cells.
Gastric ulcers
Cigarette smoking increases the chances of developing gastric ulcer as well as other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as gastritis, reflux and inflammatory bowel disease, for example, due to the increase in inflammation also in the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestine.
Therefore, it is common for people who smoke to have more symptoms like stomach pain, burning, maldigestion and changes in the bowel.
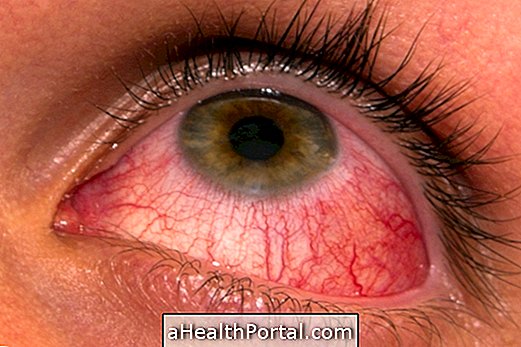
6. Visual changes
Cigarette smoke substances also increase the risk of developing eye diseases, such as cataracts and macular degeneration, by increasing the chances of cell dysfunction and inflammation.
Cataracts cause haze or blurred vision, which impairs visual ability, especially at night. Macular degeneration, on the other hand, causes changes in the center of the vision, which gets blurred and can worsen over time.

7. Memory Changes
Cigarette smoking is associated with an increased risk of developing dementias, both from Alzheimer's disease and from brain injuries from micro-strokes.
Dementia syndromes cause memory loss, which worsens over time, and can also cause changes in behavior and communication skills.
8. Complications in pregnancy
In the case of pregnant women who smoke or inhale excess cigarette smoke, cigarette toxins can cause various illnesses, such as miscarriage, fetal growth retardation, premature birth or even death of the baby, so giving up this habit is essential.
Thus, it is important to observe the presence of bleeding, intense cramps or changes in the growth of the uterus, being very important to prenatal correctly to identify any change as soon as possible.
9. Bladder cancer
Most of the carcinogenic substances in the cigarette that enter the circulation need to be eliminated as it passes through the urinary tract, increasing the chances of developing bladder cancer by coming into contact with the tissue of this organ.
Some signs that this type of cancer can present are bleeding in the urine, abdominal pain and weight loss. Learn about the other symptoms of bladder cancer.
10. Lung cancer
When cigarette substances come into contact with the fine tissues of the lungs that make the respiratory changes, there is a risk of cancer arising from the inflammation and dysfunction induced by them.
Lung cancer causes symptoms such as shortness of breath, coughing up excessive or bloody and slimming. However, the cancer is often silent and only causes symptoms when it is advanced, so it is important to stop smoking as soon as possible, in addition to regular follow-up with the pulmonologist.

Other types of cancer
Cigarette smoking causes almost 20 types of cancer, so in addition to lung cancer and bladder it increases the chances of many other types such as:
- Mouth cancer;
- Laryngeal Cancer;
- Stomach cancer;
- Mama;
- Cervix;
- Leukemia.
This is because the carcinogenic substances in the cigarette are able to interfere with the genetic information of the cells, in addition to causing inflammation.
In case of suspected illness caused by smoking or living with someone who smokes, it is important to schedule an appointment with the general practitioner or pulmonologist, so that the necessary examinations and guidelines are made to avoid or treat these situations.
How to Avoid Cigarette Illness
The only way to avoid these diseases is to stop smoking, because the risk will only decrease if you avoid the substances of this habit. Although it is difficult to abandon this addiction, one must keep in mind the importance of this attitude to health, and take the first step. Check out some tips on what to do to stop smoking.
If it is difficult to achieve alone, there are treatments that can help with smoking cessation, prescribed by the pulmonologist, such as nicotine patches, in addition to attending support groups or having psychological counseling.
Normally, when you stop smoking, the risk of diseases, especially cardiovascular and cancer, has a large decrease. So the risk is 50% lower after 2 years without smoking and and there are no more risks when the person is 10 years without the addiction.






-o-que--sintomas-transmisso-e-tratamento.jpg)