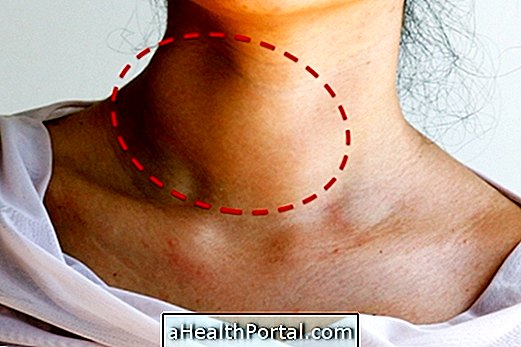
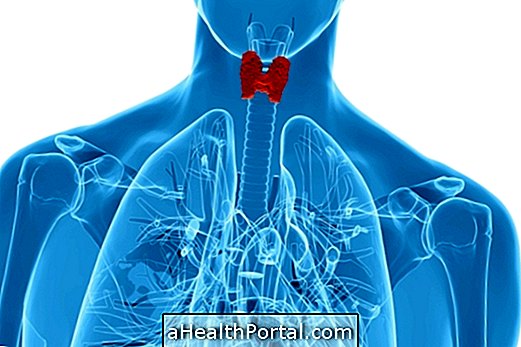
A lump in the neck may indicate a thyroid nodule, a condition that is usually benign and does not need any treatment, although it must always be evaluated by an endocrinologist or medical head and neck surgeon, because although it is not very common, it can be cancer.
Nodules are usually benign and appear with advancing age, and therefore, the onset of cancer is rare. However, it is recommended to consult an endocrinologist to confirm that the lymph node is benign or malignant through examinations such as ultrasound with biopsy and blood tests requested by the doctor.
See which signs may indicate cancer in: 7 symptoms that may indicate thyroid cancer.
Symptoms of Nodule in Thyroid
Most nodules in the thyroid do not cause any type of symptom, being identified by the presence of a 'lump' in the neck. Here's how to do the self-check to check for nodules by clicking here.
However, in some cases, thyroid nodules can produce symptoms such as:
- Sore throat;
- Swelling of the neck;
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing;
- Loss of weight without apparent cause;
- Tremors and nervousness;
- Hoarseness or loss of voice.
When a thyroid nodule is suspected, it is recommended to consult a general practitioner or an endocrinologist for tests.
What exams do you do?
The doctor can find the nodule by palpating the neck region and then request a blood test that measures the amount of TSH, T3 and T4, anti-TPO, thyroglobulin and Doppler ultrasonography and biopsy to check the size, number, consistency, define the nodule type and collect a tissue sample (biopsy) that should be evaluated in a laboratory to know if the nodule is benign or malignant. Learn about the tests that evaluate the thyroid.
Signs that the lump may be cancer
Some signs that may indicate that the lump may be malignant and that it is cancer are when:
- Fast growing hard nodule:
- Age less than 20 or over 60 years;
- The nodule has irregular borders;
- There are changes in the voice such as hoarseness or paralysis of the vocal chords;
- Other cases of thyroid cancer in the family;
- The person has already had radiotherapy in the region of the head and neck.
There are studies that indicate that the higher amount of TSH indicates that the nodule may be malignant, however many people diagnosed with thyroid cancer have never had changes in blood tests or biopsy, only finding after the analysis done after removing the nodule .
When the patient has only 1 nodule up to 1 cm in diameter, as long as it is not malignant, the doctor may not indicate any type of treatment, indicating only thyroid ultrasonography and annual blood tests.
Thyroid Nodule Types
When identifying a nodule in the thyroid one should evaluate its classification through Doppler ultrasonography to determine if it is benign, malignant and what therapeutic measures to adopt. The classification can be made:
| According to Lagalla et al | According to Chammas et al |
| Type I: Absence of vascularization | Pattern I : Absence of vascularization |
| Type II: Perinodular vasculature | Pattern II: Peripheral vascularization only |
| Type III: Peri and intranodular vascularization | Standard III : Peripheral vasculature greater than or equal to central |
| --- | Standard IV: Greater than peripheral central vasculature |
| --- | Standard V: Central vascularity only |
The endocrinologist may also classify the thyroid nodule as:
- Hypoechoic: mass less dense than bone and, therefore, the lump may be filled by liquid or air;
- Isoechoic: solid mass with the same density as the bone and which usually has a circular shape;
- Hyperechoic: mass with a higher density than the bone, and may indicate a thyroid nodule with calcification.
Nodes with central vascularization are more likely to be malignant tumors.
How to treat thyroid nodule
The treatment is only used when the person has symptoms, when there is a risk of cancer in the thyroid or when the nodule is more than 1 cm. The most commonly used treatments include:
- Surgery : It is used especially for nodules larger than 3 cm and in cases of malignant nodule to remove all cancer cells, but can also be used to treat benign nodules when they cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing, because they are very large. Learn all about surgery for removal of the thyroid nodule.
- Levothyroxine Remedies, such as Synthroid or Levoid: Prevents the production of TSH, the hormone that causes thyroid tissue to grow, and is widely used in cases of benign nodules that are increasing in size.
After treatment with surgery, it may be necessary to have hormonal replacement as well as to have regular consultations, at least twice a year, at the endocrinologist or head and neck surgeon.
Here's how to prevent and treat thyroid problems in the following video:

What are the causes of thyroid nodule?
The causes are not yet fully known, but it is known that women are the most affected and that those who have other people in the family with thyroid nodules are more likely to develop nodules like this.
How the thyroid nodule affects pregnancy
The woman who has a lump in this gland is no more difficult to conceive than the others. However, the presence of a thyroid nodule during pregnancy can cause changes in the production of hormones and, if this happens, the pregnant woman should take medicines that help regulate thyroid function, preventing the baby from being born with a delay in physical development or mental, for example.











-o-que--como-identificar-e-o-que-fazer.jpg)