Edwards Syndrome, also known as trisomy 18, is a very rare genetic disorder that causes delays in the development of the fetus, resulting in severe malformations such as microcephaly and heart problems, which can not be corrected and, therefore, there is a low expectation of life.
Generally, Edwards Syndrome is more frequent in pregnancies in which the pregnant woman is more than 35 years old. So, the best way to try to prevent the onset of this syndrome is to become pregnant before that age.
Edwards syndrome has no cure, so the baby born with this syndrome has a low life expectancy because normally less than 10% can survive up to 1 year after birth.
Main Characteristics of Edwards Syndrome
Some of the features of Edwards Syndrome are:
- Small head and narrow;
- Mouth and small jaw;
- Long fingers and poorly developed thumb;
- Feet with rounded sole;
- Cleft palate;
- Problems in the kidneys, such as polycystic kidneys, ectopic or hypoplastic kidneys, renal agenesis, hydronephrosis, hydroureter or doubling of ureters;
- Cardiac diseases, such as defects of the ventricular septum and ductus arteriosus or polyvalvular disease;
- Mental disability;
- Breathing problems due to structural changes or absence of one of the lungs;
- Difficulty sucking;
- Weeping;
- Low weight at birth;
- Brain changes such as cerebral cyst, hydrocephalus, anencephaly;
- Facial paralysis.
Usually the doctor suspects Edward Syndrome by ultrasonography, where nuchal translucency can be measured, but blood tests are also performed to evaluate human chorionic gonadotrophin, alpha-fetoprotein and unconjugated estriol in maternal serum in the 1st and 2nd trimesters of pregnancy. Tests that can confirm the syndrome are puncture of the chorionic villi and amniocentesis.
Fetal echocardiography, done at 20 weeks' gestation, may show the cardiac involvement, which is present in 100% of the cases of this syndrome and therefore is considered as the primary exam for the diagnosis of this syndrome after 18 weeks of gestation.
How is Edwards Syndrome treated?
There is no specific treatment for Edwards Syndrome, however, the doctor may recommend medications or surgery to treat some problems that threaten the baby's life in the first few weeks of life. Usually the baby is frail and needs specific care most of the time, so he may need to be hospitalized for appropriate treatment without suffering.
In Brazil, after the diagnosis, the pregnant woman can make a decision to go to court and request an abortion if the doctor identifies life-threatening or serious psychological problems for the mother during pregnancy.
What causes this syndrome
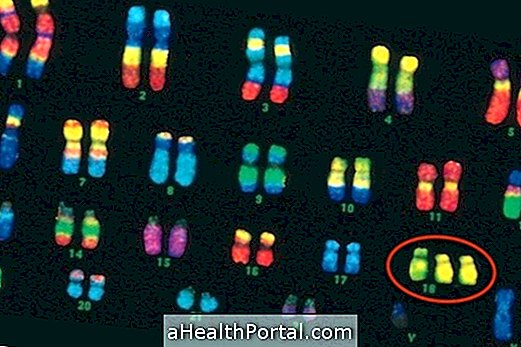
This syndrome is caused by the appearance of 3 copies of chromosome 18, and normally there are only 2 copies of each chromosome. This change happens in a random way and, therefore, it is unusual for the case to be repeated within the same family.
Because it is a completely random genetic change, Edwards Syndrome is nothing more than parents to children. Although it is more common in children of women who become pregnant more than 35 years old, the disease can occur at any age.










-o-que--como-identificar-e-o-que-fazer.jpg)