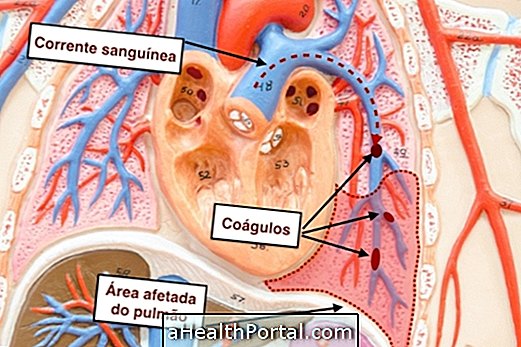
Treatment should be started as soon as possible in the emergency room as soon as the first symptoms of embolism appear, such as severe shortness of breath or coughing up blood. Learn more about the symptoms that identify the embolism.
This treatment is done with injections of thrombolytic medicines, such as Urokinase or Alteplase, which help dissolve the clot that is preventing blood from reaching the lung.
If the clot can not be removed with medication alone, a minor surgery may be necessary under local anesthesia, where the doctor inserts a thin flexible tube through an artery in the arm or leg into the clot in the lung, removing -O.
This emergency treatment should be started as soon as possible to relieve symptoms and avoid serious complications such as cardiac arrest.
How is home treatment done?
After eliminating the clot from the lung, it is usually necessary to be hospitalized for at least 2 to 3 days to ensure that no new clots arise and to ensure that the levels of oxygen in the body are normalized.
After this, the doctor usually recites anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin or heparin, which should be done daily at home, accordingly and which prevent the blood from getting too thick and re-forming clots.
In addition to these, your doctor may also recommend pain relievers, such as Tramadol or Acetominofene, to relieve chest pain within the first few days after treatment.
Signs of improvement
Symptom improvement comes a few minutes after emergency treatment with relief of breathing difficulty and decreased chest pain.
Signs of worsening
The signs of worsening are increased difficulty breathing and, finally, fainting, due to the decrease in the amount of oxygen in the body. If treatment is not started quickly, serious consequences such as life-threatening cardiac arrest may occur.