A uterine biopsy is a diagnostic test used to identify laboratory abnormalities in uterine lining tissue that may indicate abnormal growth of the uterus, infections of the uterus, and even cancer. Learn all about this procedure in What It Is and What the Biopsy Is for.
Usually, uterine biopsy is recommended by the gynecologist when abnormal changes occur in the female reproductive system, such as excessive bleeding outside the menstrual period, pelvic pain or difficulty getting pregnant, for example.
Biopsy of the uterus can be painful, so in some cases the doctor may use local anesthesia to reduce the discomfort of the woman.
How is the biopsy of the uterus
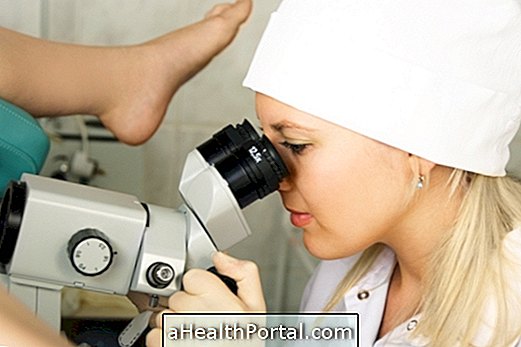
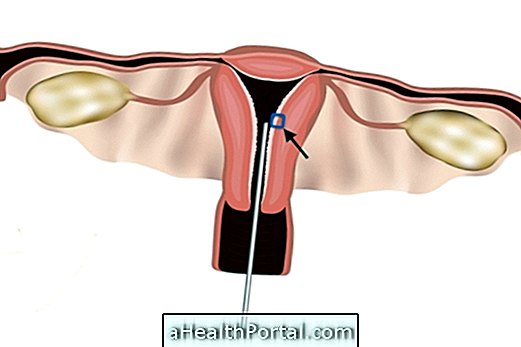
The biopsy of the uterus is usually done in the gynecologist's office, as follows:
- The woman is placed in the gynecologist's chair without panties but covered by a sheet;
- The gynecologist inserts a small lubricated device into the vagina, called a speculum;
- The doctor does a lavage of the cervix and applies the local anesthesia, which can cause a small abdominal cramp;
- The gynecologist inserts another device into the vagina, known as a colposcope, to remove a small piece of tissue from the uterus.
Usually the biopsy lasts about 5 to 15 minutes and after the examination the doctor places the sample taken in a vial that will be sent for analysis under the microscope in the laboratory.
Result of biopsy of the uterus
The main results of uterine biopsy are:
- Negative or normal biopsy: there are no changes in the cells of the uterus or any other type of lesion and the uterus has the thickness necessary for the moment of the menstrual cycle in which the woman is;
- Positive or abnormal biopsy: This result may have several meanings, such as uterine polyp, abnormal growth of uterine tissue, HPV infection, cervical cancer, or uterine cancer.
The outcome of the uterine biopsy should always be evaluated by a gynecologist to make the correct diagnosis and initiate appropriate treatment.
Here's how to identify early signs of uterine problems:
- Symptoms of infection in uterus
- Symptoms of cervical cancer