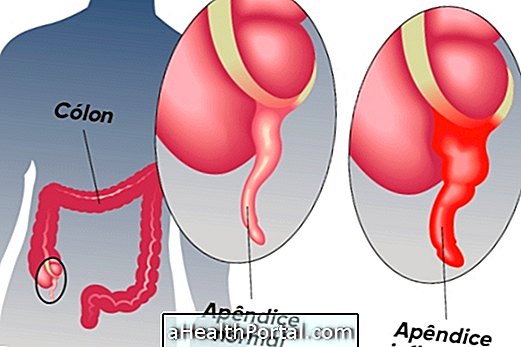
The appendix is a small, tube-shaped pouch about 10 cm long, which is attached to the first part of the large intestine, close to where the small, large intestine binds. This way, your position is usually under the lower right region of the belly.
Although not considered an essential organ for the body, when it is inflamed it can be life-threatening due to the high chance of bursting and releasing bacteria through the abdomen, resulting in a generalized infection. Thus, it is important to be aware of the first signs of inflammation, also known as appendicitis, such as very severe pain in the lower right region of the belly, vomiting and lack of appetite. Check for any symptoms that may indicate an appendicitis.
What is it for
There is no agreement on the exact functions of the appendix, and for many years it was believed that it did not play any important role for the organism. However, over time, and through various studies, there have been several theories about the functions of the appendix, such as:
1. Remains of human evolution
According to this evolutionary theory, although the appendix has no function at present, it has served to digest food in the past, especially in times when humans fed mainly on plants, having an important role in the digestion of the hardest parts such as bark and roots, for example.
Over time, the diet of humans was altering and containing other foods easier to digest in the stomach and, therefore, the appendix was no longer necessary and ended up getting smaller and becoming only a vestigial organ without a specific function.
2. Immune system organ
In more recent research, it has been proven that the appendix contains lymphoid cells, which are important in helping the body fight infection. Thus, the appendix can play an important role in strengthening the immune system.
These cells accumulate in the appendix after birth to adulthood, around the age of 20 or 30 years, helping in the maturation of other cells of the immune system and in the formation of antibodies of the IgA type, which are very important to eliminate viruses and bacteria mucous membranes such as the eyes, mouth and genitals, for example.
3. Organ of the digestive system
According to other studies, the appendix may also function as a reservoir of good bacteria for the intestine, and is used when the body undergoes an infection that causes changes in the gut microbiota, as it happens after intense diarrhea.
In these cases, the appendix releases its bacteria so they can grow and develop in the intestine, taking the place of the bacteria that were eliminated with the infection and eventually functioning as a probiotic.
When to have surgery to remove
Surgery to remove the appendix, also known as appendectomy, should be done only when the appendix is inflamed, as there is a high risk of bursting and causing a generalized infection. In these cases, the use of antibiotics usually has no effect and, therefore, cure is only achieved with surgery.
Therefore, appendectomy should not be used as a prevention method to avoid appendicitis in the future, as the appendix may have some important function and should only be removed when in fact it is a health risk.
Learn more about this surgery and how to recover.