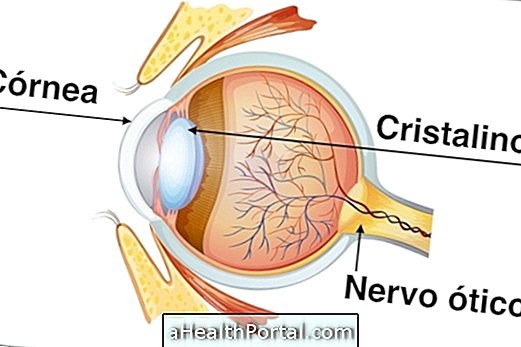
Glaucoma eye drops have the function of reducing blood pressure in the eyes, and should be used throughout life to control the disease and prevent its main complication, which is blindness.
However, although they help control the disease, eye drops also cause various side effects such as headache, drowsiness and itching, but it is important to continue using the medication correctly until you see your ophthalmologist to see if you can make changes to the treatment.
Types of Eye Drops
There are 6 types of eye medications that can be used according to the health characteristics of the patient, such as the presence of asthma, allergies, heart problems and bronchitis.
1. Alpha agonists
They are especially recommended for patients who are allergic to preservatives used in other eye drops, and some examples of such medications are Alphagan, Alphagan P, Combigan.
Side effects: Burning and burning in the eye after application, fatigue, headache, drowsiness, dry mouth and dry nose.
2. Beta-blockers
They act by reducing the production of fluid inside the eye, and some examples are Timoptol, Nyolol, Betoptic.
Side effects: Decreased blood pressure, reduced heart rate and fatigue. In people with a history of asthma, it can also cause mild shortness of breath.

3. Prostaglandin Derivatives
They act by increasing the withdrawal of the liquid that is produced in the eye, which helps to decrease the pressure, and some examples of this type of remedy are Lumigan, Xalatan, Travatan.
Side effects: Yellow eye, burning, blurred vision, redness of eyes, itching and burning.
4. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
They may be used both in the form of eye drops and in the form of tablets, and some examples of such medicaments are Trusopt, Cosopt, Azopt.
Side effects: Burning and burning in the eyes.
5. Cholinergic or Miotic
They work by increasing the withdrawal of the liquid that is produced in the eye and may also be used together with other glaucoma remedies, and some examples of this type of eye drops are Isopto Carpine, Isopto Carbachol.
Side effects: Vision darkened, especially at night or in poorly lit places.
6. Combined formulas
They are medicines that use more than one type of active principle, and some examples are Cosopt, Combigan, Simbrinza.
Side effects: Burning and burning eyes, blurred vision, eye irritation, changes in taste and dry mouth.
How to use
To improve the efficacy of the medication, eye drops should be shaken before use and dripping only 1 drop at a time into the lower eye, the red pouch that forms when pulling the lower eyelid down.

The ideal is to lie down during the application, and after dripping the drop should close the eye and press the corner near the nose, as this causes the medicine to be absorbed in the place, reducing the side effects that occur when it passes to the bloodstream.
If the drop falls out of the eye, you should drip again, remembering also to do at least 5 minutes between applying different eye drops.
Food aid in the treatment of Glaucoma
To help control the disease, you should maintain a balanced diet rich in antioxidant foods and with important nutrients for the eyes, such as vitamins A, C and E, and minerals zinc and selenium.
What to eat
These nutrients are present mainly in orange and red foods like orange, pineapple, carrot, acerola, pumpkin, strawberry, goji berry and raspberry. In addition, by improving circulation and being an antioxidant, cranberry also helps improve night vision and eye brightness and can be used to relieve the symptoms of glaucoma.
What to avoid
It is important to avoid consuming foods high in sugar and large amounts of liquids and caffeine in a short time as this increases blood pressure and pressure in the eye.
Thus, it is recommended to drink small amounts of liquid throughout the day to maintain hydration and consume a maximum of 2 to 3 cups of coffee per day, avoiding excessive consumption of other foods containing caffeine such as cola, green tea, black tea and chocolate.
Physical Activity Fights High Blood Pressure
Frequent physical activity helps reduce eye pressure and can control risk factors for glaucoma, such as diabetes and high blood pressure. Thus, it is recommended to do exercises such as walking or cycling for at least 40 minutes, 4 times a week.
In addition, it is important to avoid exercises in positions that leave the body upside down, such as during yoga or pilates classes, as this may increase pressure on the head and eye, requiring medical authorization before practicing this type of activity physics.
See other types of treatment for Glaucoma.