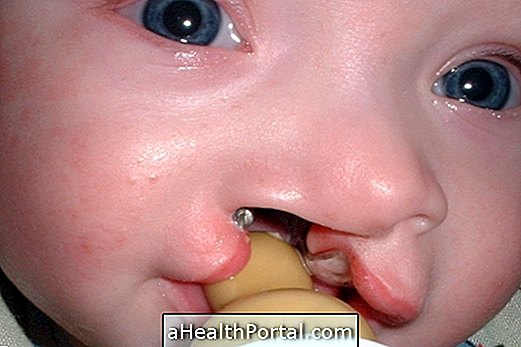
Arrinia is a congenital, severe and rare condition in which the baby is born without a nose. The arrinia can be diagnosed in the prenatal examination, being recommended the realization of the child as soon as identified so that the risks for the newborn are reduced.
Arrinia can be classified in:
- Arrinia, in which the baby is born without the nasal pyramid, ie, the nose itself;
- Total arrinia, which is characterized by the absence of the nose and lack of formation of the olfactory system.
Since it has no specific cause, arrinia has no established treatment, but a tracheostomy is usually performed soon after birth so that the baby can breathe while eating, for example. In addition to the absence of nasal structures, other conditions may be associated, such as malformations of the central nervous system and hypogonadism, which is characterized by decreased production of sex hormones, for example.

Possible causes
Arrinia is an extremely rare condition and is believed to be a multifactorial disease, ie it depends on genetic and environmental factors to occur.
Regarding genetics, in some cases inversion or trisomy of chromosome 9 was observed, and in other cases, translocation between chromosomes 3 and 12, all of these genetic alterations being determinant for the occurrence of structural alterations such as arrinia. However, in some cases of arrinia no inversion, trisomy or translocation were observed, which makes the cause of this condition still a reason for research.
Arrinia can also occur due to malformation during the development process of the fetus, having no relation to genetics.
Associations of arrinia
Some babies are born with the nose but are not born with the olfactory organs and usually happens in association with other malformations, such as:
- Hypertelorism, which is characterized by malformation of the skull and consequent removal of the eyes in excess;
- Hypogonadism;
- Changes in the nervous system;
- Cryptorchidism, in which there is no descent of the testicles to the scrotum - know how the treatment of cryptorchidism is done;
- Coloboma of the iris, in which there is alteration in the structure that sustains the iris, changing its form. Understand what coloboma is and how to treat it;
- Microphthalmia, which is a congenital malformation in which one or both eyes are smaller than normal.
The diagnosis of arrinia can be made from the second trimester of pregnancy through ultrasound examination or after birth by means of computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, in which it is checked if there is complete or partial absence of the nasal structure.
After birth, the baby is intubated via orotracheal and submitted to mechanical ventilation and then a tracheostomy can be performed to allow the baby to breathe. In addition, a nasal prosthesis may be used until the baby is old enough to perform a surgical repair that aims to form the nasal structures.