Cardiac arrhythmia has a cure but should be treated as soon as the first symptoms appear to prevent possible complications caused by the disease, such as heart attack, stroke, cardiogenic shock and death. See when the arrhythmia can be serious.
The treatment of cardiac arrhythmia will depend on the severity of the symptoms, whether or not the association with other heart diseases and type of arrhythmia, which may be:
- Benign arrhythmia, in which changes in heart rate may even disappear spontaneously, and may be easily controlled with medications indicated by the physician and regular physical activity. However, there should be periodic consultations with the cardiologist so that periodic cardiac exams are performed so that the activity of the heart is evaluated and there is a need to perform some type of surgical procedure;
- Malignant arrhythmia, in which the changes do not disappear spontaneously and worsen with the exertion or practice of physical exercises, being able to lead to the death if it is not treated quickly and in the correct way.
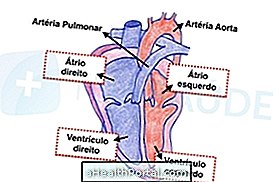
The arrhythmia corresponds to changes in the heart rate, making the heart rate faster, slower or even stopping the heart, which leads to symptoms such as tiredness, chest pain, pallor, cold sweat and shortness of breath. Learn how to identify cardiac arrhythmia.

Treatment Options
Treatment options vary according to the symptoms presented, with the following behaviors being more common:
- Electric shock, electrical cardioversion or defibrillation : it has the function to reorganize the heart rhythm in some types of arrhythmias more urgent, as in the cases of atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia. Learn how the heart defibrillator works;
- Medications : Propafenone, Sotalol, Dofetilide, Amiodarone and Ibutilide are the main medicines that can be indicated by the cardiologist for symptom control and regularization of heartbeats;
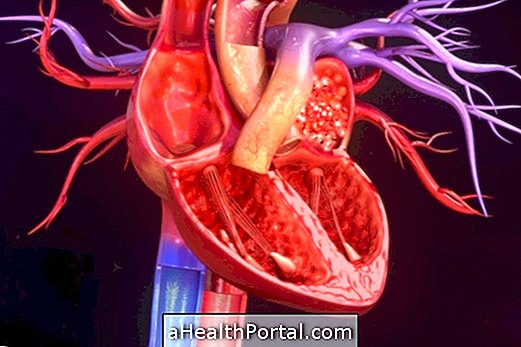
- Implantation of an artificial pacemaker : The pacemaker is a device with a long-lasting battery whose function is to take charge of the heart as the doctor prescribes, regulating the heart rate and allowing the person to lead a normal life. See what pacemaker care;
- Cauterization or ablation surgery: in which a localized and precise burn is made, which will prevent or hinder new arrhythmia attacks. The procedure lasts a few hours, and sedation or general anesthesia may be necessary.
Other important measures to treat and avoid arrhythmia are changes in lifestyle, ie avoid alcohol, drugs, caffeinated beverages, black tea and cigarettes. In addition, it is important to practice regular physical activities and have a balanced diet.