Treatment for stroke or stroke should be started as soon as possible, so it is important to be able to identify the first symptoms to call an ambulance immediately, because the earlier you start treatment, the lower the risk of sequelae such as paralysis or difficulty speaking, or more serious complications such as coma and death. Here are the signs that can indicate a stroke.
Thus, the treatment can be started by the doctor already in the ambulance on the way to the hospital, with medicines such as antihypertensives to stabilize blood pressure and heart rate, use of oxygen to facilitate breathing, and control of vital signs as a form to restore blood flow to the brain.
After the initial treatment, the type of stroke should be identified through examinations such as tomography and resonance, as this influences the next steps of the treatment, explained in detail below. In addition, it is very important that rehabilitation therapies be initiated as soon as possible, such as with physical therapy or occupational therapy, for example, which decreases the effects of the day-to-day of the person.
Treatment for ischemic stroke
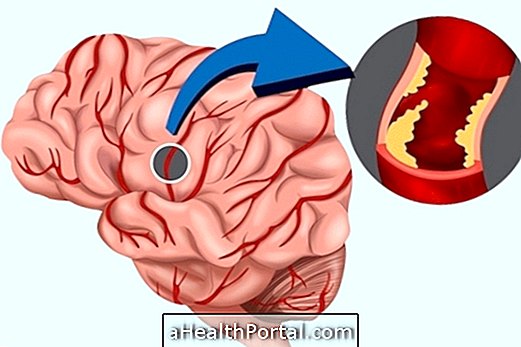
Ischemic stroke arises when a vein in the brain becomes obstructed and blood can not reach a part of the organ, which is almost always due to a thrombus or clot. In such cases, one or more of these forms of treatment may be used:
- Tablets, such as AAS, Clopidogrel and Simvastatin: used in cases of suspicion of this type of stroke or transient ischemia, as they are able to control the formation of the clot and prevent further occlusion of the cerebral vessels;
- Thrombolysis with APT injection is an enzyme that should be administered only when ischemic stroke is already confirmed by tomography and should be used within the first 4 hours because it rapidly destroys the clot, improving blood circulation to the affected area and decreasing the sequelae;
- Cerebral catheterization : In some hospitals, as an alternative to APT injection, it is possible to insert a flexible tube that runs from the groin artery to the brain to try to remove the clot or to inject anticoagulant medicines on the spot. Learn more about cerebral catheterization;
- Blood pressure control with antihypertensives, such as captopril: is done in cases where blood pressure is high, to prevent this high blood pressure from worsening oxygenation and blood circulation in the brain;
- Monitoring : monitor the vital signs of the person who has had a stroke, observing heart rate, blood pressure, blood oxygenation, blood glucose and body temperature, keeping them stable until the person shows some improvement because if they are uncontrolled, there may be a worsening of the stroke and the caused sequel.
After a stroke, brain decompression surgery is indicated in cases where the brain has a large swelling, which increases the intracranial pressure and can cause risk of death. This surgery is done by removing for a period part of the skull bone, which is restored when the swelling improves.
Treatment for hemorrhagic stroke

The cases of hemorrhagic stroke arise when a cerebral artery presents a blood leak or ruptures, as it happens with an aneurism or due to peaks of high pressure, for example.
In these cases, the treatment is done by controlling blood pressure, such as antihypertensives, in addition to using an oxygen catheter and monitoring vital signs so that bleeding is controlled more quickly.
In more severe cases where there is complete rupture of the artery and it is difficult to stop bleeding, it may be necessary to have emergency brain surgery to find the bleeding site and correct it.
In cases of large haemorrhagic stroke, brain decompression surgery can also be done, as it is common to have irritation and swelling of the brain through bleeding.
How is the recovery from stroke?
Generally, after acute stroke symptoms have been controlled, hospital admission is required for about 5 to 10 days, which varies according to the clinical condition of each person to be observed, in order to guarantee an initial recovery and to assess the consequences of stroke.
During this period, the physician may initiate the use of medication or may adjust the patient's medications, recommending the use of an antiaggregant or anticoagulant, such as aspirin or warfarin, in the event of an ischemic stroke, or removing the anticoagulant, in case of Haemorrhagic stroke, for example.
In addition, remedies may be needed to better control blood pressure, blood glucose, cholesterol, for example, to reduce the risk of new stroke episodes.
Some sequelae may remain, such as difficulty speaking, decreased strength on one side of the body, changes in food swallowing or for controlling urine or feces, as well as changes in thinking or memory. The amount and severity of sequelae vary according to the type of stroke and the affected site of the brain, as well as the body's ability to recover from the person. Understand better the possible complications of stroke.
Rehabilitation to reduce sequelae
After a stroke, a person needs to do a series of rehabilitation processes to accelerate recovery and reduce sequelae. The main forms of rehabilitation are:
- Physiotherapy : Physiotherapy helps to strengthen muscles, so that the person can recover or maintain the movements of the body, improving their quality of life. See how physiotherapy is done after a stroke.
- Occupational Therapy : is an area that helps the patient and the family to find strategies to reduce the effects of daily stroke, through exercises, home adaptation, restroom, and activities to improve reasoning and movement;
- Speech therapy : this type of therapy helps to recover speech and swallowing of patients who have had this area affected by stroke;
- Nutrition : After a stroke, it is important that the person has a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals that nourish the glass and healthy way to avoid malnutrition or a new stroke. In some cases where it is necessary to use a probe to feed, the nutritionist will calculate the exact amount of food and teach how to prepare.
Family support is critical in this recovery period from a stroke, both to help in activities that the person can no longer perform and to emotional support, as some limitations can be frustrating and cause feelings of helplessness and sadness. Learn how to help someone who has difficulty communicating.