The main causes that can lead to preterm birth, which occurs when the baby is born with less than 37 weeks of gestation, are related to events and diseases that endanger the life of the mother.
Women who are most at risk of having a preterm birth are the history of previous preterm birth, twin pregnancy, and blood loss through the vagina in the third trimester of pregnancy. In addition, when the woman is over 35 years or less than 16, she is more likely to have a preterm birth, requiring medical follow-up every 2 weeks.
Some of the maternal causes of preterm birth are:
- Premature rupture of the amniotic sac;
- Incompetence of the cervix;
- Uterine infection;
- Placental abruption;
- Pre eclampsia;
- Anemia;
- Diseases such as tuberculosis, syphilis, renal infection;
- Pregnancy of twins or more babies;
- In vitro fertilization;
- Fetal malformation;
- Intense physical exertion;
- Use of illicit drugs and alcoholic beverages;
- Uterine fibroids;
- Previous caesarean section;
- Bacterial vaginosis;
- Presence of group B streptococci.
Vaginal infections increase the risk of preterm delivery due to the presence of toxins that may promote the release of cytokines and prostaglandins that trigger labor.
It is important to remember that the consumption of flaxseed oil in pregnancy also increases the chances of preterm delivery, and therefore its consumption is contraindicated at this stage.
What to do if you think you are in labor
If the woman suspects that she is in labor and has not yet completed 37 weeks of gestation, she should call her obstetrician and go to the hospital as soon as possible so that he can examine and decide what to do. Some signs that may indicate a premature birth are uterine contractions, pain or discomfort in the belly or back and vaginal discharge.
Find out how the diagnosis of preterm birth is made
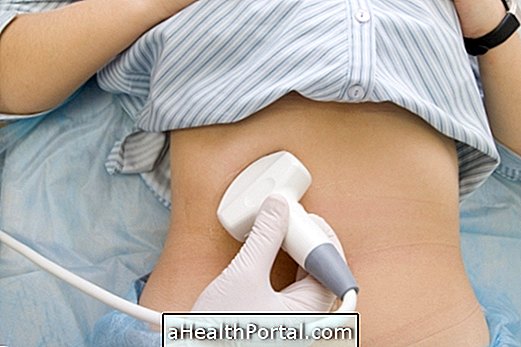
To make sure there is a risk of preterm birth and decide what to do in that case the doctor can evaluate the uterine cervix through transvaginal ultrasound and the presence of fetal fibronectin can be seen in the vaginal secretion.
Measurement above 30 mm in the cervix indicates a higher risk of delivery within 7 days and women who present this value should be evaluated for fibronectin. If the woman has measurements between 16 and 30 mm but negative fetal fibronectin has low risk of delivery, however, when fetal fibronectin is positive, there is risk of delivery in 48 hours.
Find out what the doctor can do to prevent premature delivery and what the consequences are for the unborn baby by clicking here.