There are several diseases that fungi can cause in humans, and most are mycoses in the skin, nails, mucous membranes or scalp, such as white cloth, had, frieira, thrush or candidiasis, for example.
Fungi generally coexist harmoniously with the body, but can cause disease when they can bypass the protective barriers of the body, which occurs mainly during periods of immunity or injury to the skin.
In addition, although fungal infections are mostly superficial and easily treated, there are fungal species that can cause deep lesions and even reach the bloodstream and organs such as lungs, such as sporotrichosis, histoplasmosis, or aspergillosis, for example.
Although there are numerous diseases caused by fungi, some of them are:
1. White cloth
Also known as beach mycosis, this infection has the scientific name of Pteriasis versicolor, and is caused by the fungus Malassezia furfur, which causes round spots on the skin. Usually the spots are white, as the fungus prevents the production of melanin when the skin is exposed to the sun, and are more common in the trunk, abdomen, face, neck or arms.
- How to treat : The treatment is usually done with antifungal creams or lotions, such as Clotrimazole or Miconazole, indicated by the dermatologist. In the case of very large lesions, the use of tablets, such as Fluconazole, may be indicated.
Understand better about what white cloth is and how to treat it.
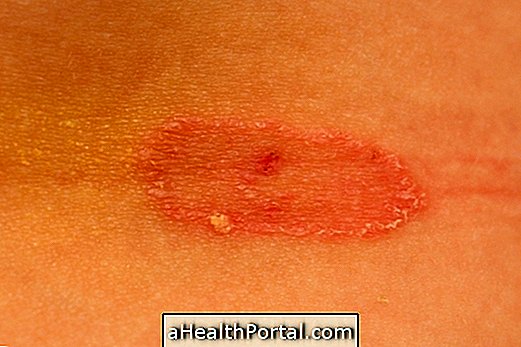
2. Had
Scientifically called dermatophytosis, this fungal infection is also known as tinea, and can target various body sites such as skin, hair and nails, and is caused by fungi such as Trichophyton, Mycrosporon or Epidermophyton, which are transmitted from one person to another through contaminated soil and animals.
Some of the main injuries are:
- It had corporeal, also called impingem and appears on any area of the skin.
- It had the feet, also called a chilbler or athlete's foot, which is located between the toes;
- It had cruris, which develops in the groin;
- It had capitis, or scalp, which is more ocmum in children and can cause hair loss on the spot;
- It had nails, which makes the nail thick and dull.
The injury that arose in the patient had a scaly, reddish and itchy skin. Generally, without proper treatment, the lesion spreads slowly, and is very contagious.
- How to treat: The treatment is made with antifungal ointments, such as Miconazole, Clotrimazole or Itraconazole, and can last for weeks to months. When there is a serious infection, or when the nails are very affected, tablet medications such as Fluconazole, Itraconazole, or Terbinafine may be needed. During the treatment it is essential to dry the feet well after bathing and to avoid closed shoes for a long time.
Learn more about the types of had and how to identify.
3. Candidiasis
There are several species of fungi that are part of the Candida family, the most common being Candida albicans . Although it naturally inhabits the body, especially the mucosa of the mouth and the intimate region, these fungi can cause various types of infection in the body, especially when immune defenses are impaired.
The most affected body regions are folds of the skin, such as groin, armpits and between the fingers and toes, and nails, and can also reach mucous like mouth, esophagus, vagina and rectum. In addition, infection can be serious to the point of spreading through the bloodstream to reach organs such as the lungs, heart or kidneys.
- How to treat : The treatment is mainly made with antifungal ointments such as Fluconazole, Clotrimazole, Nystatin or Ketonoconazole. However, in more severe cases or in infection in the blood and organs of the body, antifungal tablets or vein may be needed.
Learn more about how the treatment for candidiasis is done.
4. Sporotrichosis
This ringworm can overtake the skin and also reach the subcutaneous region and the lymph nodes. This infection is caused by fungi of the family Porothrix spp ., Which inhabit nature and are present in the soil, plants, leaves and wood, for example, so they infect mainly farmers, gardeners or farmers.
This fungus can also be transmitted by the scratching of contaminated cats. Generally, the infection of the skin causes the appearance of painless, reddish and gradually growing lump. In some cases, especially in people with compromised immunity, a number of lesions can arise, as well as spread through the bloodstream and infect the lungs, bones, joints, testes, and even the brain.
- How to treat : Treatment with oral or intravenous antifungals, such as Itraconazole, for 3 to 6 months, and in severe cases may require the use of antifungal venous, such as amphotericin B, and may last for 12 months.
Check out more details on what is sporotrichosis, symptoms and how to treat.

5. Aspergillosis
It is the infection caused by the Aspergillus fungus, which mainly affects the lungs, although it also causes allergies or reaches other regions of the airways, causing sinusitis or otitis, for example.
This fungus is found in the environment, and may even be indoors, in humid environments such as wall corners or bathrooms. When invading the lungs through respiration, Aspergillus causes lesions, called fungal balls or aspergillomas, which can cause coughing, shortness of breath, bloody phlegm, weight loss, and fever.
- How to treat : Treatment is done with potent antifungals such as Itraconazole or Amphotericin B, doctor-directed.
Check out more about the symptoms of Aspergillosis and how to treat it.
6. Paracoccidioidomycosis
Also called South American blastomycosis, this infection is caused by fungi of the family Paracoccidioides, which inhabits the soil and plants, so it reaches more people in the rural area.
Transmission occurs mainly through the air, when the fungus is inhaled, which penetrates the lungs and bloodstream, causing symptoms such as lack of appetite, weight loss, coughing, shortness of breath, fever, itching, skin sores and the appearance of gums.
- How to treat : To treat this infection, your doctor will advise you to use antifungals such as Itraconazole, Fluconazole, Ketoconazole or Voriconazole, for example, and the treatment can last for months to years.
Understand better what paracoccidioidomycosis is, how to identify and treat it.
7. Histoplasmosis
It is an infection caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum, which is transmitted through the inhalation of fungi present in nature.
The disease usually develops in people with weakened immunity, such as by immune diseases, AIDS or malnourished, for example, or people who inhale a large amount of fungi. The signs and symptoms that can occur are cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, sweating, fever and weight loss.
- How to treat : The treatment is done with the use of systemic antifungals like Itraconazole, Ketonocazol or Amfotericina B, for example.
Learn more about Histoplasmosis.