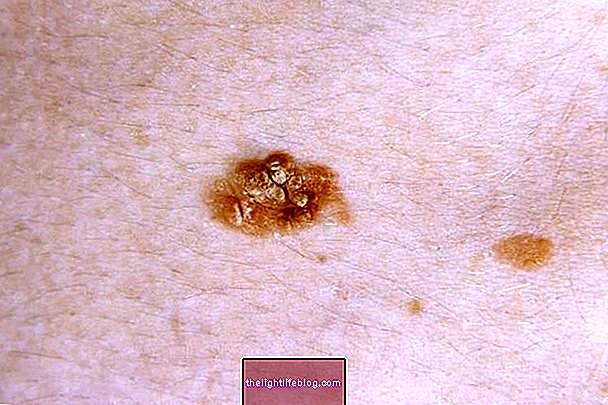
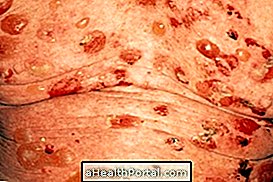
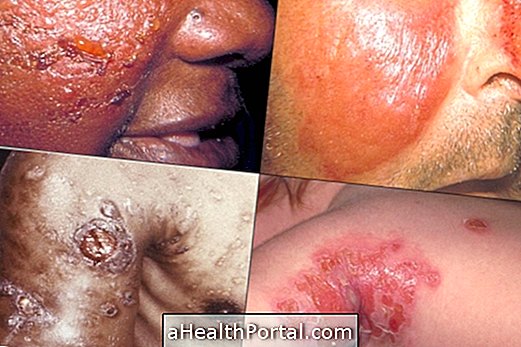
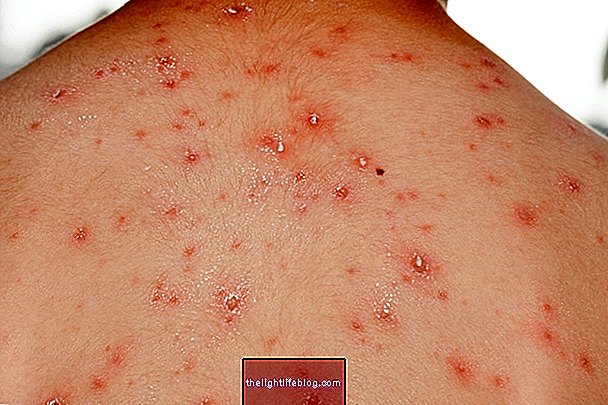
Pharmacodermia is a set of reactions of the skin and the body caused by the use of drugs, which can manifest in a variety of ways, such as red spots on the skin, lumps, rashes, or even skin detachment. very serious.
Any medication can trigger these reactions in the skin, but the ones that most commonly cause these problems are antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, anticonvulsants and psychotropics like Amoxicillin, Aspirin, Ciprofloxacin, Penicillin or Sulphonamides, for example.


Signs and symptoms
Pharmacoderma can manifest itself in different ways, and the main types of presentation are:
- Urticaria : It forms spots or reddish, scattered or localized plaques, which can cause a lot of itching, being the most common type of manifestation of allergy;
- Acneiform eruption : causes lesions, called rashes, in the form of vesicles and which have the appearance of pimples;
- Erythroderma : is another type of rash that leaves the skin of the whole body reddish, followed by a peeling;
- Erythema pigmentosa or multiforme : appearance of reddish or purplish circular spots, with a small bubble in the center, common in the palms of the hands. It is common for the person to have the spot in the same place when using the medicine again;
- Erythema nodosum : presence of hardened nodules that are under the skin, with a reddish or purplish color;
- Bullous eruptions : blisters of various sizes and shapes, which are at risk of inflammation and infection;
- Photosensitivity : stains of varied colors, such as red or brown, triggered after exposure to the sun.
These reactions may be accompanied by other symptoms such as generalized itching, swelling in the mouth or eyes, difficulty breathing, fever in excess of 40 ° C, joint pain, or in more severe cases, difficulty in blood clotting.


To diagnose these changes, caused by medications, the general practitioner or dermatologist should exclude other causes of skin blemishes such as Zika virus infections, measles and reactions to products or clothing, for example. See which diseases cause red patches on the skin.
In addition, there are some severe syndromes that may appear in some people due to the use of medicines, such as:
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome : presence of spots, blisters and even detachment of the skin, which may appear in the mucous membranes of the mouth;
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis : there is also detachment of the skin, which is very intense and causes wounds that can reach the whole body, associated with fever, sore throat, cough and burning eyes;
- Hypersensitivity to Drugs or DRESS : is a reaction characterized by red spots, fever, enlarged lymph nodes, and inflammation of organs such as hepatitis.
These types of reactions are most common in people who have a change in immunity, such as people with HIV, babies, the elderly, or those who have a history of food allergies.
How is the treatment done?
Generally, pharmacodermia is resolved after discontinuation of the drug, or it is also possible to alleviate symptoms with anti-allergic or corticoid use, for example as prescribed by the physician.
In addition, during treatment, it is recommended that the person follow a light diet, with fewer products that can worsen skin reactions or cause allergies more easily, such as processed products, inlays, canned, milk, peanuts and tomatoes, for example. example. See what kind of nutrition you should have to improve dermatitis.
Signs of improvement
Signs of improvement begin to appear when new lesions stop and lesions progressively decrease. It is common, however, that some types of stains last for some time, especially when they are dark residual stains or when they are triggered by the sun.
After the improvement, it is important to keep an appointment with the dermatologist, who can request an examination to evaluate the types of allergy that the person has, to better guide the medicines or products that should be avoided. See how the allergy test is done.
Signs of worsening
There is a risk of worsening in cases where the lesions may increase, or when the symptoms accompanying the skin lesions worsen, such as swelling, fever, and joint pain. In such cases, the emergency department should be taken to the emergency room as soon as possible for treatment with medicinal products, such as antiallergics and corticosteroids, to prevent the reaction from progressing and to prevent it from becoming severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylactic shock or glottal edema. example.