Calcitonin is a hormone produced in the thyroid that has the function of lowering the concentration of calcium in the blood, decreasing the absorption of calcium by the intestines and preventing the activity of osteoclasts.
Thus, calcitonin is very important for the maintenance of bone health, and so there are medicines with this hormone in the composition, which are used in diseases such as osteoporosis, Paget's disease or Sudeck syndrome, for example.

What is it for
Calcitonin medicines are used to treat diseases such as:
- Osteoporosis, or associated bone pain, in which the bones are very thin and weak;
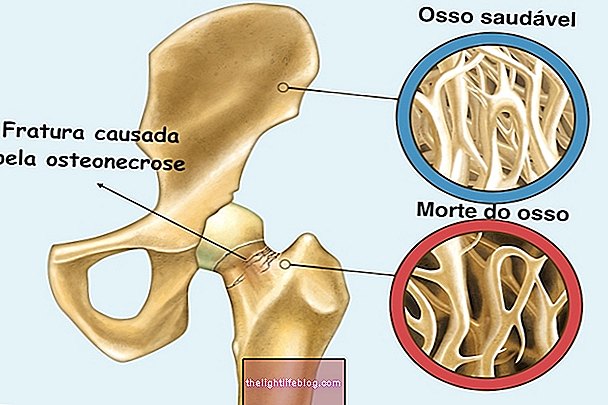
- Paget's bone disease, which is a slow, progressive disease that can cause changes in the size and shape of certain bones;
- Hypercalcemia, which is characterized by a very high value of calcium in the blood;
- Reflex symptomatic dystrophy, which is a disease that causes pain and changes in bone, which may involve local bone loss.
Calcitonin has the function of regulating calcium levels in the blood and is therefore used to reverse bone loss. In addition, it is also believed that this hormone is also involved in bone formation.
When not to use
Generally, calcitonin used in the medications with this hormone is salmon calcitonin, and therefore it is contraindicated in people with allergy to this substance, or to any other component of the formula.
In addition, it is also not recommended for pregnant women, women who are breast-feeding, and people under 18 years of age.
How to use
The recommended dose of calcitonin depends on the problem to be treated:
- Osteoporosis: The recommended dose is 50 IU per day or 100 IU per day or every two days by subcutaneous or intramuscular injection.
- Bone pain: The recommended dose is 100-200 IU per day by slow intravenous infusion in physiological saline solution or by subcutaneous or intramuscular injection in divided doses distributed throughout the day until a satisfactory response is obtained.
- Paget's disease: The recommended dose is 100 IU per day or every two days by subcutaneous or intramuscular injection.
- Emergency treatment of hypercalcemic crisis: The recommended dose is 5 to 10 IU per kilogram of body weight per day, by intravenous infusion, for at least 6 hours, or by slow intravenous injection in 2 to 4 divided doses throughout the day.
- Prolonged treatment of chronic hypercalcemia: The recommended dose is 5 to 10 IU per kilogram of body weight per day, by subcutaneous or intramuscular injection, as a single dose or as two divided doses.
- Reflex symptomatic dystrophy: The recommended dose is 100 IU per day by subcutaneous or intramuscular injection for 2 to 4 weeks.
It is up to the doctor to determine how long the treatment should be continued.
Possible side effects
The most common side effects that can occur with calcitonin are dizziness, headache, changes in taste, redness of the face or neck, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, bone or joint pain, and tiredness.
In addition, although less often vision disturbances, high blood pressure, vomiting, muscle, bone or joint pain, flu symptoms, and swelling of the arms or legs may also occur.
When the calcitonin test is done
Calcitonin titration is indicated mainly to identify and monitor the presence of medullary thyroid carcinoma, a disease that causes significant elevations of this hormone.
In addition, calcitonin may also be useful for identifying other conditions, such as thyroid C-cell hyperplasia, which are calcitonin-producing cells, as well as for other cancers such as leukemia, lung cancer, breast, pancreas or prostate, for example. Learn more about what the calcitonin test is for and how it is done.