Hemorrhagic fever is a serious condition characterized by the onset of fever above 38 ° C, pain in the whole body and bleeding from the eyes, mouth, nose, urine and vomiting, which can result in severe bleeding if left untreated.
Generally, hemorrhagic fever is caused by potentially fatal diseases caused by viruses, such as Ebola, Dengue or Marburg Disease.
Hemorrhagic fever has a cure but should be treated in isolation in the hospital. In Brazil, hemorrhagic fever is more frequent during Dengue, and there are still no cases of Ebola hemorrhagic fever.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic fever
Symptoms of hemorrhagic fever may include:
- High fever, above 38ºC, and sudden;
- Bleeding from the eyes, mouth, nose, ears, urine and feces;
- Bruising on the skin;
- Severe headache;
- Excessive tiredness and muscle pain;
- Vomiting and diarrhea with blood;
- Skin rashes.
The patient with symptoms of hemorrhagic fever should consult a general practitioner as soon as possible to diagnose the problem and initiate appropriate treatment, since after a few days hemorrhagic fever can cause stopping of various organs such as liver, spleen, lungs and kidneys, as well as such as severe brain changes.
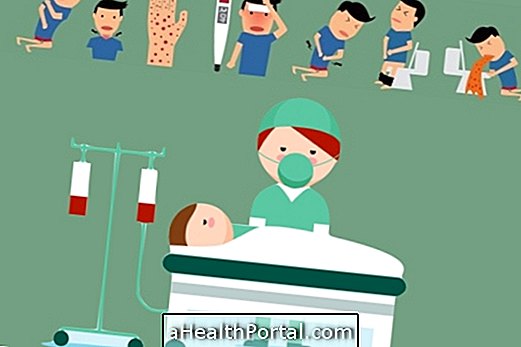
How To Treat Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever
Treatment for haemorrhagic fever should be directed by a general practitioner or an infectious specialist, but is generally done in hospital isolation with blood transfusions and analgesic remedies in the vein to control bleeding and hemorrhagic fever symptoms.
In addition, in some diseases, antiviral drugs may still be used to help the body fight the virus that is causing the hemorrhagic fever. However, some diseases, such as Ebola or Dengue, do not yet have a specific treatment, and it is necessary to wait until the patient's organism cures the disease.
Learn more about diseases that cause hemorrhagic fever:
- Ebola virus
- Marburg disease
- Symptoms of dengue