Cystitis is a bladder infection, usually caused by bacteria, which is characterized by pain and burning when urinating, blood in the urine, turbid, smelly urine, and frequent urination.
It is recommended that cystitis be treated early on to prevent damage to the kidneys, for example. The diagnosis of cystitis is made through urinalysis, in which the characteristics of urine and the presence of microorganisms are evaluated.
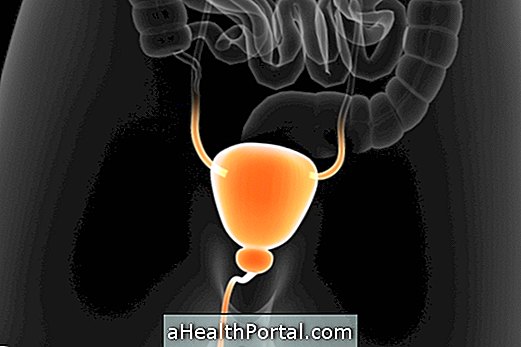
Symptoms of cystitis
Symptoms of cystitis, which is inflammation of the bladder, usually caused by a bacterial infection, are similar in man and woman, including:
- Frequent urge to urinate, but little urine volume;
- Pain or burning when urinating;
- Presence of blood in the urine;
- Urine dark, cloudy and with a very intense smell;
- Pain in the back of the belly or feeling of heaviness;
- General malaise or weakness.
In addition, in adults, although fever may occur, it is usually not higher than 38 ° C, however when there is a high fever or back pain, it may be indicative of impaired kidneys.
In children, cystitis can be very difficult to identify because they are very vague and the child has difficulty explaining what they feel. However, some signs that may indicate this problem include peeing in the pants during the day, presenting a fever above 38 ° C, feeling very tired or being more irritated, for example.
How is the diagnosis made?
The initial diagnosis of cystitis is done by assessing the symptoms presented by the person. To conclude the diagnosis, the doctor usually asks for the urine test, also called EAS, so that the characteristics of the urine are analyzed, as well as to identify if there are signs of infection.
Usually when the urine test is verified the presence of numerous pyocytes, erythrocytes, positive nitrite and presence of bacteria, and indicative of infection. However, the diagnosis can only be concluded by means of uroculture examination, in which urine is analyzed at the microbiological level, in which tests are carried out to identify the microbial species causing the infection, as well as to verify the sensitivity profile of the microorganism, indicating the best antimicrobial to be used in the treatment.
Although urine exams are the primary forms of diagnosis for the identification of the disease, cystitis can also be caused by the use of medications or diabetes and is the result of a negative urine test. Therefore, it may be recommended by your doctor to perform ultrasound of the bladder to check for signs of inflammation in the bladder. If it exists, the doctor will assess the family and individual history to identify the cause and thus start treatment.
In the case of cystitis caused by microorganisms, the initial treatment is done with the use of Ciprofloxacin, however, after the uroculture is usually recommended more specific medicine for the treatment. See what other cystitis pills are.
What can cause cystitis
In most cases, cystitis is caused by a bacterial infection in the bladder, but other causes may be:
- Frequent use of medications, especially chemotherapeutics, such as Cyclophosphamide or Ifosfamide;
- Menopause, because the urethra become more susceptible to infections;
- Diabetes, because high blood sugar levels increase the risk of infections in the body;
- Chemical irritation, such as the use of soaps or perfumes in the intimate region that imbalance pH;
- Injuries caused by sexual intercourse or use of a bladder catheter, for example.
Depending on the cause, treatment should be adapted and therefore, whenever symptoms arise it is advised to consult the doctor to confirm the cause of the problem and initiate the appropriate treatment.