Lactose intolerance is the body's inability to digest the sugar in milk, lactose, causing symptoms such as colic, gas and diarrhea, which appear moments after eating this food. To confirm the presence of lactose intolerance, the diagnosis can be made through examination of stool, blood test, respiratory test or biopsy of the intestine.
Although usually diagnosed in childhood, adults may also develop lactose intolerance, with more or less intense symptoms according to the severity of intolerance.
1. Observe the symptoms of lactose intolerance
The symptoms of lactose intolerance may manifest themselves more or less intensely according to the degree of the incapacity of the production of lactase, an enzyme that digests cow's milk, they can be:
- Colic - abdominal pain;
- Intestinal gases;
- Acid Diarrhea.
These symptoms usually appear moments after the ingestion of cow's milk, dairy products or products that are prepared with milk. so if you experience these symptoms, try taking the food exclusion test for 7 days to see if the symptoms disappear.
2. Take the Food Exclusion Test
If you suspect that you do not digest cow's milk well, try not to consume this milk for 7 days. If within these days you have no symptoms, take a test and drink some milk and then wait to see the reaction of your body. If the symptoms return, you may have lactose intolerance and you may not be able to ingest cow's milk.
This test can be done with all foods that are prepared with milk, such as cheese, butter, pudding and delicacy, for example. And depending on your degree of lactose intolerance, the symptoms may be more or less intense.
3. Go to the doctor and do exams
To make sure it is lactose intolerance, in addition to taking the food exclusion test, you can take tests such as:
- Stool test : measures the acidity of faeces being very common to detect lactose intolerance in infants and young children.
- Exhaled Air Test : Measures the abnormal presence of hydrogen in the exhaled air after the ingestion of lactose diluted in water. Learn how to take this exam.
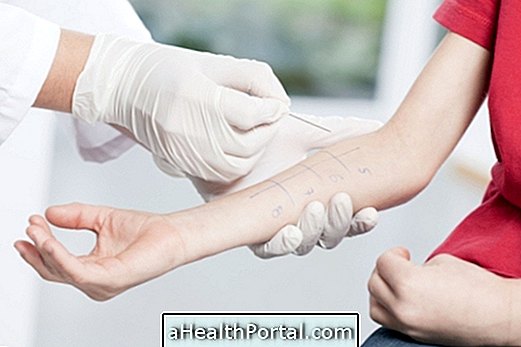
- Blood test: measures the amount of glucose in the blood after taking lactose diluted in water in the laboratory.
- Intestinal biopsy : In this case a small sample of the intestine is examined under the microscope to identify the presence or absence of specific cells that determine lactose intolerance. Although very useful it is less used because it is more invasive.
These tests may be requested by the general practitioner or allergist in case of suspected lactose intolerance or when the food exclusion test leaves some doubts.
It is very important to diagnose and treat lactose intolerance because it is a condition that causes unpleasant symptoms and affects the absorption of important nutrients for the body.
Treatment for lactose intolerance
The treatment of lactose intolerance is the exclusion of cow's milk and everything prepared with cow's milk such as cake, biscuit, wafer and pudding, from the food. However, sometimes the person may take a supplement of lactase, which is an enzyme that digests milk, when it needs or wants to eat some food prepared with cow's milk.
The lactase can be can be bought at the pharmacy or pharmacy handling and is very easy to use. This enzyme can be added to the cake recipe or can be ingested just before eating these foods. Some examples are Lactrase, Lactosil and Digelac. Another possibility is charcoal capsules relieve symptoms after the person has ingested some source of lactose and may be helpful in an emergency.


Cow's milk is rich in calcium, which is important for maintaining bone health, so people who have lactose intolerance should increase their intake of other source foods such as prune and blackberry. See other examples in: Foods rich in calcium.
However, there are several levels of lactose intolerance, and not everyone needs to stop eating dairy products such as cheese and yogurt because these foods have a lower amount of lactose, and it is possible to eat a small amount at one time or another.
Here's how to ingest the amount of calcium needed in the video:

Breast milk also has lactose, but to a lesser extent, so mothers who breastfeed children who have lactose intolerance can continue breastfeeding without problems, eliminating dairy foods from their own diet.
Here's how you can ensure your calcium intake:
- Tips for Improving Calcium Absorption
- How to make a calcium-rich diet to ensure strong bones