To see if you are obsessed with healthy eating you need to notice signs like avoid eating out of the house and only consume organic foods. This obsession with healthy eating is called orthorexia nervosa, which is an eating disorder where there is an exaggerated concern about the quality of food.
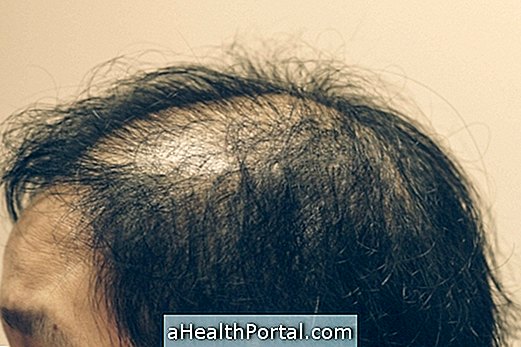
Orthorexia can lead to health problems like lack of vitamins and minerals, anemia and hair loss, for example. This disorder should be treated with medical and psychological follow-up, and the family support to identify and overcome this problem is important.

What is Ortorexia?
Orthorexia is a type of eating disorder that arises when there is an excessive preoccupation with food, having as main characteristic the exaggerated pursuit to always eat healthy. In addition, there is also a concern to always have pure food, without pesticides, contaminants or products of animal origin.
This food restriction is intensified and the individual with this disorder ends up having a little varied diet, not consuming foods like milk, meat, sugar, trans fat and processed, which can lead to weight loss and lack of vitamins and minerals.
Another characteristic of this syndrome is the exaggerated concern with the way of food preparation, taking excessive care not to add too much salt, sugar or fat, in addition to avoiding eating outside the home.
Signs and Symptoms of Orthorexia
The main symptoms of orthorexia are:
- Seek to know and follow the rules of healthy eating;
- Exclude foods perceived as impure, which are normally those containing dyes, preservatives, trans fats, sugar and salt;
- Prefer organic products, excluding transgenic foods and agrochemicals;
- Avoid eating out of the house or take your own food when going out with friends;
- Plan meals several days in advance;
- Exclude food groups from the diet, especially meats, milk and dairy products, fats and carbohydrates.
This over-concern with diet can lead to nutritional deficiencies, causing diseases such as anemia and osteopenia, which are fragile bones in adults.

Diagnosis of orthorexia
The diagnosis of orthorexia is made by the physician through a detailed assessment of the patient's eating habits to see if there are dietary restrictions and over-concern with food. A physical examination is also done to check for signs of lack of nutrients, such as hair loss and brittle nails.
In addition to the clinical evaluation, it is also necessary to do blood tests to check for nutrient deficiencies in the body or health problems such as anemia.
Treatment of orthorexia
The treatment of orthorexia nervosa should be done with medical follow-up, also being necessary in some cases the psychological accompaniment. It is common to take nutritional supplements in cases where there are deficiencies in nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, or the presence of diseases such as anemia.
In addition to medical follow-up, family support is also essential for orthorexia to be identified and overcome, and healthy eating is done without endangering the patient's health.
It is also important to remember that orthorexia is different from vigorexia, which is when there is an excessive search through physical activity to have a full body of muscles.














-o-que--causas-e-tratamento.jpg)




