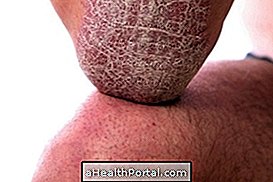
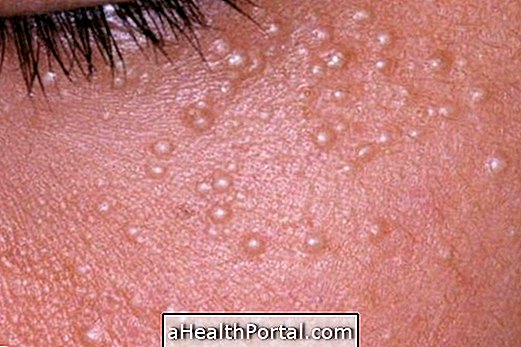
Atopic dermatitis, or atopic eczema, is a form of inflammation of the skin caused by an allergic reaction of this organ, being more common in adults and children who also have allergic rhinitis and asthma.
In this way, this disease is not contagious, and presents in a cyclical way, that is, it has periods of improvement and worsening. Its main symptoms are:
- Redness on the spot;
- Small lumps or bubbles;
- Localized swelling;
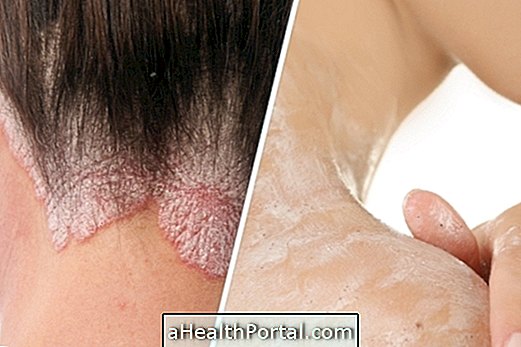
- Desquamation of the skin;
- Itching;
- Crusts may form;
- There may be thickening or darkening of the skin in the chronic phase.
The main sites affected by dermatitis are the folds of the body, such as the elbows, knees or neck, or on the palms and soles of the feet; however, in the most severe cases, it can reach several places on the body.

Atopic dermatitis in the baby
Most often, atopic dermatitis occurs in infants as early as the first year of life, or in children up to 5 years of age, and may last through adolescence, but in some cases they may last a lifetime.
Childhood atopic dermatitis can occur anywhere on the body, being common on the face, cheeks and the outer parts of the arms and legs.


What are the causes
Atopic dermatitis is a genetic and hereditary disease, however, it may appear and disappear according to some stimuli, such as:
- Dry skin;
- Dusty environments;
- Detergents, cleaning agents and other chemicals in contact with the skin;
- Very dry, humid, hot or cold environments;
- Heat and sweat;
- Skin infections caused by fungi or bacteria;
- Some foods that cause allergy;
- Stress and anxiety.
These triggering factors vary from person to person, and therefore, the reason that leads to the outbreak of dermatitis may be different for each case.
Thus, for dermatitis to be controlled, it is very important to move away from these situations, as well as using skin moisturizers and anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory remedies in ointment or tablet prescribed by the dermatologist. Check out which remedies and ointments are most used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis.