Erythrasma is a skin infection caused by the bacteria Corynebacterium minutissimum that leads to the appearance of patches on the skin that may flake. Erythrasma occurs most often in adults, especially obese and diabetic patients, since the bacterium is usually found in which there is friction of the skin, as in the folds, that is, the axilla and under the breasts, for example.
This skin disease can be easily diagnosed by means of the Wood Lamp, which is a diagnostic method in which the lesions acquire a specific coloration when exposed to ultraviolet light. In the case of erythrasma, the lesion acquires red-coral glow, and can thus be differentiated from other lesions. Diagnosis can also be made by scraping the lesion, which is sent to the laboratory for identification of the microorganism, but is a more time-consuming method of diagnosis.

How is the treatment done?
Treatment for erythrasma is done according to the advice of the dermatologist and is usually done with the use of antibiotics such as Erythromycin or Tetracycline for 10 days or according to the medical recommendation. In addition, specific ointments for erythrasma, such as Erythromycin cream, may be recommended. If the presence of fungi in the lesion is identified, the use of antifungal creams or ointments may also be recommended by the physician.
During treatment it is advised that the person use antibacterial soaps to wash the affected region, being more recommended to use those that contain Chlorxidine.
Main symptoms
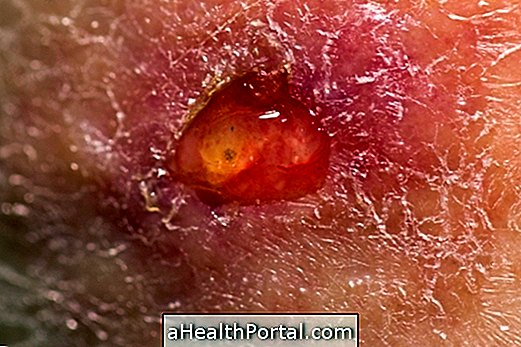
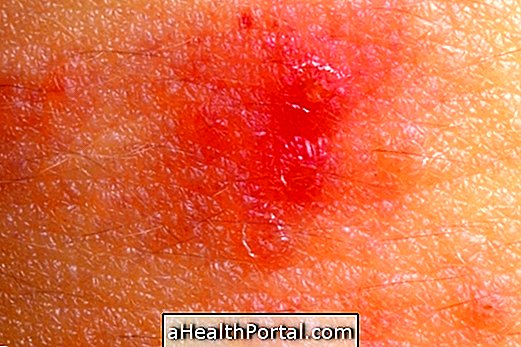
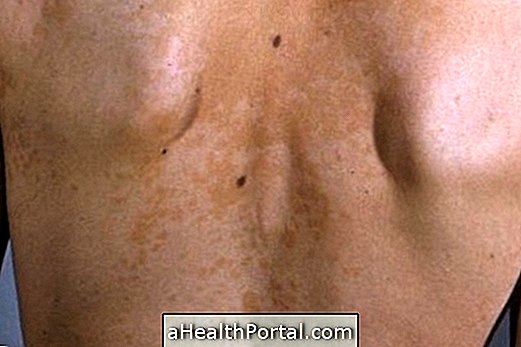
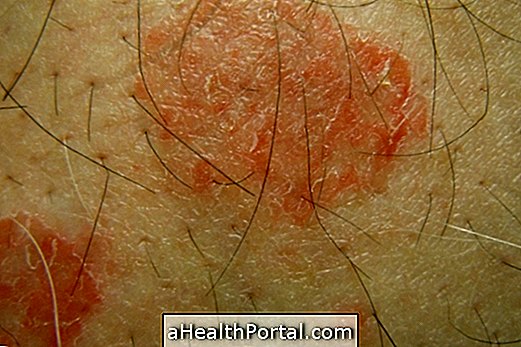
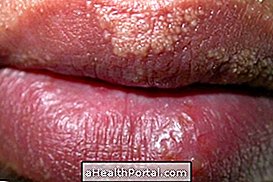
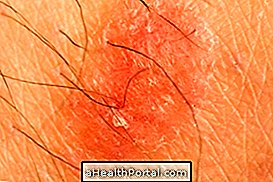
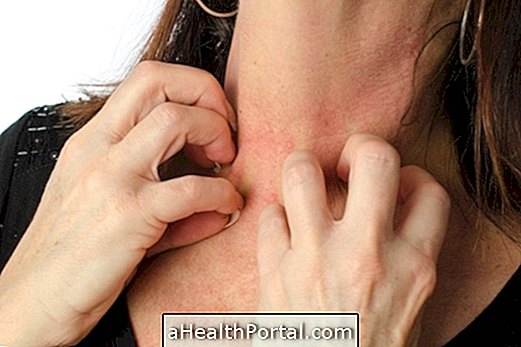
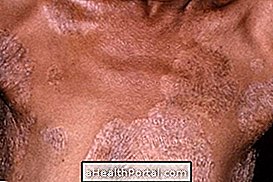
Erythrasma has as its main symptom the presence of pink or dark irregular spots that can flake and lead to the appearance of cracks in the skin. In addition, there may be slight flaking.
Lesions usually appear more frequently in regions where there is skin-to-skin contact, such as under the breast, under the armpit, between the foot, groin, and intimate regions. The great production of sweat or inadequate hygiene of these regions can also favor the appearance of erythrasma characteristic lesions.