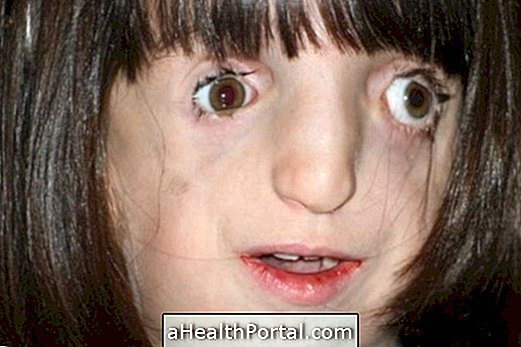
Gigantism is a rare disease in which the body has excess growth hormone, causing the organs and parts of the body to grow more than normal.
When the disease arises from birth, it is known as gigantism, but if the disease occurs in adulthood, usually around the age of 30 or 50, it is known as acromegaly.
In both cases, the disease is caused by a change in the pituitary, the site of the brain that produces the growth hormone, and therefore the treatment is done to reduce the production of the hormone, which can be done through surgery, use of medicines or radiation, for example.

Main symptoms
Adults with acromegaly or children with gigantism usually have larger-than-normal hands, feet, and lips, as well as coarse features on the face. In addition, excess growth hormone may still cause:
- Tingling or burning in the hands and feet;
- Excess glucose in blood;
- High pressure;
- Pain and swelling in joints;
- Excessive tiredness.
In addition, as there is a possibility that excess growth hormone is being produced by a benign tumor in the pituitary gland, other symptoms such as regular headaches, vision problems or decreased sex drive may also arise.
How to confirm the diagnosis
When gigantism is suspected, a blood test should be done to evaluate levels of IGF-1, a protein that is increased when growth hormone levels are also above normal, indicating acromegaly or gigantism.
After the examination, especially in the case of the adult, a CT scan may be ordered, for example, to identify if there is any tumor in the pituitary that may be altering its function.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment of gigantism varies according to what is causing the excess of growth hormone. Thus, if there is a tumor in the pituitary gland, it is usually recommended to have surgery to remove the tumor and restore the correct production of hormones.
However, if there is no reason to change the functioning of the pituitary gland or if surgery does not work, the doctor may only indicate the use of radiation or medications, such as somatostatin analogues or dopamine agonists, for example, that should be used during whole life to keep hormone levels controlled.
What Causes Acromegaly
Acromegaly and gigantism are usually caused by the presence of a tumor in the pituitary gland, which produces growth hormone, increasing its concentration in the blood and causing the organs and parts of the body to increase in excess.