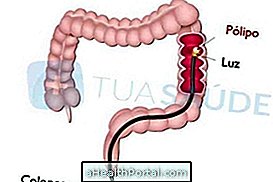
Acute diverticulitis is inflammation and infection of the diverticula, which are small folds or sacs that arise in the walls of the intestine, especially in the last portion of the colon.
These diverticula usually appear in adults over 40 years of age and do not cause symptoms, and this condition is called diverticulosis. It is also more common in people who eat a diet low in fiber or suffering from chronic constipation. Learn about the causes and symptoms of diverticulosis.
However, when diverticula are inflamed, symptoms such as pain in the abdomen, especially in the lower left side, nausea, vomiting, fever, constipation or diarrhea may occur, and in these cases, go to the emergency room immediately for treatment and avoid complications such as perforation of the intestine and infection of the body, which can be life-threatening.

How to know if it is diverticulitis
Symptoms that may alert you to an acute crisis of diverticulitis include:
- Abdominal pain, especially in the lower left side, which can be constant and persist for several days;
- Periods of diarrhea or constipation;
- Sensitivity on the left side of the abdomen;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Fever and chills.
The intensity of the symptoms varies according to the severity of the inflammation, which, if mild, may go unnoticed. However, in the presence of these symptoms it is important to go to the emergency room, where the doctor will evaluate the symptoms and, if necessary, perform ultrasound or tomography examinations of the abdomen, and blood tests that detect inflammation and infection in the intestine.
How to treat
The treatment for diverticulitis is guided by the gastroenterologist or general practitioner, and is done with:
- Use of antibiotics, such as Ciprofloxacin and Metronidazole, to control the infection for about 10 days;
- Use of analgesics, such as Paracetamol or anti-inflammatories, such as Ibuprofen, for example, to relieve abdominal discomfort;
- Caring for the diet, which in the first 3 days should be fasting or liquid, and only then gradually adding solid foods, not to increase the pressure inside the intestine. Learn what you can and can not eat during the diverticulitis crisis.
As the inflammation of the diverticula and symptoms subside, the patient should introduce high-fiber foods, such as fresh fruits and vegetables or whole grains, for example in order to prevent diverticula from inflaming again.
When the person is able to follow the guidelines well and when the condition is mild, this treatment can be done at home, however, in the case of complicated acute diverticulitis, it is important the hospitalization to perform drugs in the vein and evaluation of the possibility of surgery .
For surgical treatment of inflammation, a puncture can be made for drainage of the pus or surgery to remove the impaired part of the intestine. See more details on treatment options and surgery for diverticulitis.

How to avoid
To prevent the formation of diverticula in the large intestine, or to prevent further attacks of diverticulitis, it is important to have a high fiber diet as they stimulate the functioning and cleaning of the intestine, preventing their walls from becoming weakened and new folds forming.
For a good bowel function, it is also very important to drink plenty of fluids throughout the day, on average 2 liters of water, in addition to eating slowly and chewing well before swallowing. Here's how to make a diet rich in fiber to regulate the gut.
Also note other nutritionist tips for proper nutrition during and after treatment of diverticulitis, to prevent new seizures and improve bowel function:

Possible Complications
Throughout the picture of acute diverticulitis, the intestinal inflammation causes complications, which usually happen when it takes to start treatment or when it is done incorrectly. The main ones are:
1. Bleeding
Bleeding or bleeding from the bowel can happen even without the inflammation of the diverticulum, called diverticular bleeding, and usually manifests with the presence of blood in the stool.
What to do : Site determination and treatment for bleeding are usually done with a colonoscopy. In very severe bleeding, more complex procedures, such as angiography or even surgery, may be necessary.
2. Abscess
The abscess is an accumulation of purulent fluid, which forms in infection and inflammation of the tissue, and causes a lot of pain and fever.
What to do : To treat the abscess, it is important to use antibiotics, such as Ciprofloxacin and Metronizadol, for example, prescribed by your doctor, and in some cases drainage of the infected liquid may be necessary.
3. Fistula
Fistulas are bowel communications with other organs, which originate due to inflammation and the formation of wounds on the walls. Some symptoms are abdominal pain and the presence of feces in the urine or eliminated through the vagina, for example.
What to do : Treatment of intestinal fistula is done by coloproctologist, usually with specific surgical procedures for correction of communication depending on location and size.
4. Drilling
Drilling is a serious complication of diverticulitis, which occurs in advanced cases or that has not been treated properly, and which causes an intense abdominal inflammation due to stool that may contaminate the region.
What to do : A surgery is usually performed to correct or remove the inflamed part of the bowel.
5. Intestinal obstruction
Intestinal obstruction is also a serious complication of diverticulitis, caused by intense inflammation, which prevents the passage of liquids and feces through the intestine, which causes bloating, abdominal cramps and vomiting.
What to do : If it is a partial obstruction, treatment can be done with medicines and fasting for a period, however, in more severe obstructions, a surgical procedure is usually performed to correct the change.