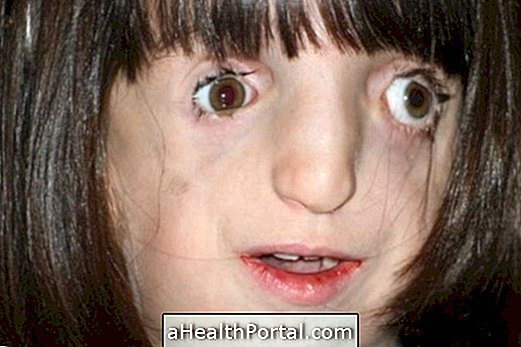
Cervical adenitis, also known as cervical lymphadenitis, corresponds to inflammation of the lymph nodes located in the cervical region, ie around the head and neck and is more commonly identified in children. Cervical lymphadenitis usually develops due to infections by viruses or bacteria, but can also be a symptom of tumors, such as what happens in lymphoma, for example. Understand what lymphoma is and how to identify it.
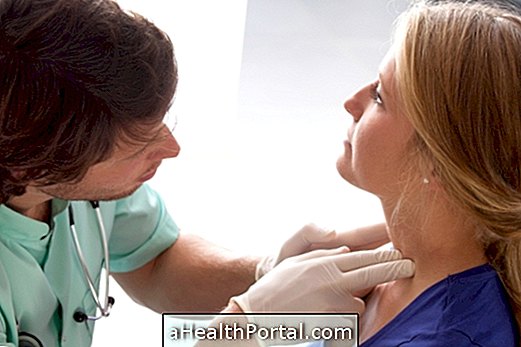
This type of adenitis is identified through palpation of the neck by the physician and association with the symptoms described by the person. It may also be necessary to perform diagnostic tests and, if tumor is suspected, tissue biopsy may be necessary to look for signs of malignancy. See what the biopsy is for and what the biopsy is for.
Main symptoms
In addition to the symptoms related to the cause of inflammation of the ganglia, cervical adenitis can be seen due to:
- Increased size of the lymph nodes, which can be seen by touching the neck, behind the ears or under the chin;
- Fever;
- There may be pain during palpation.
The diagnosis is made through the palpation of the lymph nodes located in the neck, in addition to examinations that allow to identify the cause of the swelling of the lymph nodes so that the best treatment can be established for the case. Thus, the doctor usually requests a blood test, such as the blood count, for example, besides the serology for certain bacteria and viruses and microbiological examination to verify the agent causing the infection, if cervical lymphadenopathy is the result of infection.
In addition to these tests, if the doctor checks for hemoglobin changes suspected of having a malignant process, lymph node biopsy may be necessary to check for the presence or absence of tumor cells. Here's how to identify changes in the blood count.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for cervical adenitis is intended to treat your cause. Thus, if swollen glands have occurred due to infection with bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus sp ., The doctor may indicate the use of antibiotics capable of fighting these bacteria. In the case of cervical adenitis caused by HIV infection, Epstein-Baar or cytomegalovirus, for example, the use of antivirals is recommended. In addition, the physician may recommend the use of anti-inflammatories to relieve the symptoms of inflammation.
If cancer cells that are indicative of thyroid cancer or lymphoma are reported in the test results, for example, the doctor may choose to surgically remove the lymph node or tumor that is causing it to swell, as well as perform chemotherapy sessions. Learn how it is made and what are the side effects of chemotherapy.