Hemorrhage is the loss of blood that happens after a wound, trauma or some disease, due to the rupture of vessels from the bloodstream. It can be external, when the bleeding is visualized out of the body, or internal, when it happens into some cavity of the organism, as in the abdomen, skull or lung, for example.
In venous or arterial haemorrhage, there may be large bleeding, and it is important to go to the emergency room for suturing and, in some cases, more severe surgery.
How Hemorrhage Occurs
The hemorrhage happens due to an injury of different vessels of the blood circulation, being able to be:
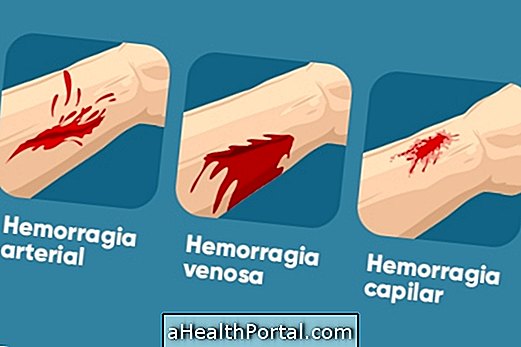
1. Capillary
It is the most common bleeding, which happens on a daily basis, usually due to small cuts or abrasions, in which only the small vessels that reach the surface of the body, called capillaries, are affected.
- What to do : Because this type of bleeding is mild and of small amount, it usually stops on its own after 5 to 10 minutes. Wash the area with soap and water and then cover with a clean dry dressing.
2. Venous
It is the hemorrhage that happens due to some great or deeper cut, with bleeding in continuous flow and slow, sometimes of great volume, through the wound.
- What to do : This type of bleeding is only serious when a large vein is reached, and therefore, it usually stops with the compression of the place with a clean cloth. You should seek the emergency room because it is usually necessary to perform a suture of the wound so that there is no risk of infection or rebleeding.
3. Arterial
It is the type of hemorrhage in which the arteries, vessels that carry blood from the heart to the rest of the body, are reached, and therefore have bright red blood with great flow and intensity. Arterial bleeding is the most serious type, and can even cause blood jets to distant parts of the body and risk of death.
- What to do : As it is a severe bleeding, it should be stopped as fast as possible, with the strong compression of the place with clean cloths or with the realization of a tourniquet, because it is a hemorrhage of more difficult control. You should go to the emergency room quickly or call 192. If bleeding is on an arm or leg, you can lift the limb for ease of containment.
The tourniquet should not be kept too long, since if it is absent for a long period of time, it can cause death of the tissues of the limb, which reinforces the importance of reaching the emergency room quickly.
There is also hemorrhage of the mixed type, which is when more than one type of vessel is reached, usually due to some accident or strong stroke, and may be more difficult to identify.
See more on how to get first aid for bleeding and other common household accidents.
Signs and symptoms of bleeding
The symptoms caused by bleeding depend not only on the origin, but also on its location, and can be classified as:
External bleeding
When the hemorrhage is external, one can easily notice its presence by the exteriorization of blood. Its amount and intensity depends on the type of vessel affected, and whether it is a region of the body with many vessels. For example, cuts on the scalp cause more bleeding, even though they are small because it is a very vascularized region.
Internal bleeding
When it is internal, it can be more difficult to identify, but the signs that indicate the presence of a hemorrhage of this type are:
- Pallor and tiredness;
- Fast and weak pulse;
- Accelerated breathing;
- Very thirst;
- Pressure drop;
- Nausea or vomiting with blood;
- Mental confusion or fainting;
- Lots of pain in the abdomen, which gets hard.
If you suspect internal bleeding, you should seek the emergency room as soon as possible, so that the procedures or surgeries necessary for it to be contained can be performed.
One of the most common forms of internal bleeding is the cerebral, which leads to the onset of a hemorrhagic stroke. Learn how to identify the first signs of stroke.

Other types of bleeding
There are also some examples of internal hemorrhages that appear, and the most common include:
- In the stool, due to a lesion in the intestine or hemorrhoids, for example, which is low digestive hemorrhage;
- In coughing, also known as hemoptysis, which happens due to respiratory infections, lung lesions or cancer, for example;
- In the uterus, due to menstrual changes or fibroids, for example;
- In the urine, caused by infections or urinary calculi;
- In the nose, or epistaxis, due to sneezing or irritation of the mucosa of the nose, for example. Learn what to do to stop bleeding in the nose.
In the presence of these types of bleeding, one should also seek the emergency room for the doctor to request tests that indicate the cause of the bleeding.





.jpg)