Anthrax is a very serious disease, which causes severe impairments of the lungs, skin and intestine. This disease intoxicates the body, and is caused by Bacillus anthracis, a bacterium that normally lives in soil and vegetation.
Due to its toxic action, it is known of the possibility of this bacterium being used as a biological weapon, having already been spread through the dust, in letters or objects. This poisoning is serious and fatal, which is a criminal act and prohibited by the United Nations.
How Transmission Happens
A person can be infected by this bacteria when they come into contact with contaminated objects or animals, which are usually cows, goats and sheep. Although it causes a serious infection, anthrax is not transmitted from person to person.
Contamination by Bacillus anthracis can be through contact with the skin, through breathing, through the lungs or through ingestion of meat or derivatives of contaminated animals.
Main symptoms
Symptoms may begin to manifest between 12 hours to 5 days after exposure to the bacteria, which can cause the disease in 3 distinct ways:
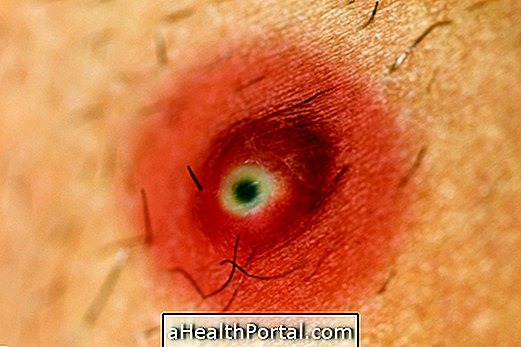
- Cutaneous anthrax : It happens when there is a skin infection, which starts as reddish brown lumps and blisters, which can rupture and form dark and painful ulcers on the skin, accompanied by swelling, and reach up to 3 cm in diameter. It can also cause muscle aches, headache, fever, nausea and vomiting.
- Pulmonary anthrax: After reaching the lungs by breathing, they may initially cause a cold-like condition, and as they thrive in the lungs and reach the bloodstream, they cause a severe picture of fever, difficulty breathing, and coma.
- Gastrointestinal anthrax : Bacteria toxins in the intestine cause an acute inflammation of this organ, which causes bleeding, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain and fever.
If the bacteria reach the brain after reaching the bloodstream, it can cause a very serious brain infection and meningitis, which is almost always fatal. In addition, all these manifestations are very serious and, if not quickly identified and treated, can lead to death.
How to identify
To diagnose Anthrax, a skin scraping, and analysis of respiratory secretions and blood tests are done to identify the causative bacteria and antibodies.
How is the treatment done?
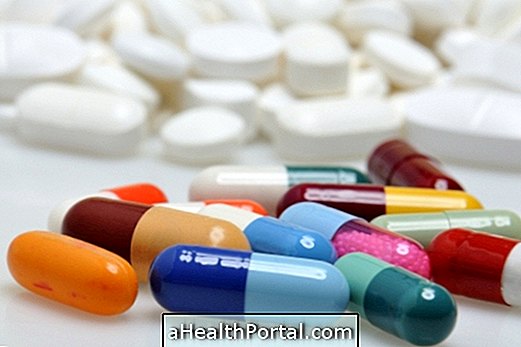
Anthrax infection is treated with antibiotics such as penicillin or doxycycline, for example, as well as drugs to try to neutralize the action of the bacterial toxin prescribed by the treating physician.
As there are still no vaccines or ways to prevent this infection, new cases should be prevented with the control of the health of the animals that can be contaminated, in an attempt to reduce the presence of this bacteria in the environment.