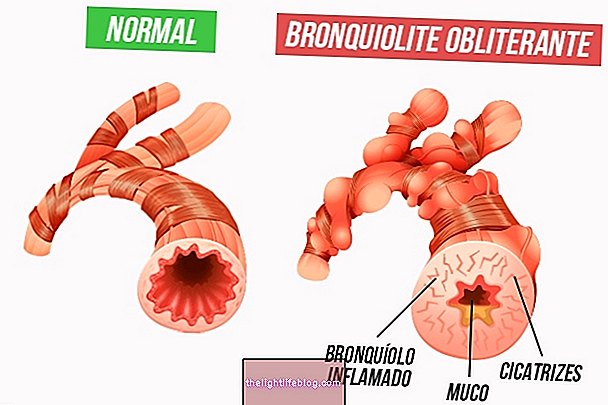
Bronchiolitis obliterans is a type of chronic lung disease in which the lung cells cannot recover after inflammation or infection, with obstruction of the airways and causing difficulty in breathing, persistent cough and shortness of breath, for example.
In these cases, the inflamed cells of the lung, instead of being replaced by new cells, die and form a scar, which hinders the passage of air. Thus, if there are several inflammations in the lung over time, the number of scars increases and the small channels of the lung, known as bronchioles, are destroyed, making it difficult to breathe.
It is important that bronchiolitis obliterans be identified and treated according to the doctor's recommendation, as this way it is possible to avoid complications and promote quality of life.

Symptoms of bronchitis obliterans
Most of the time the initial symptoms of bronchiolitis obliterans are similar to any other lung problem, including:
- Wheezing when breathing;
- Feeling of shortness of breath and difficulty breathing;
- Persistent cough;
- Periods of low fever up to 38ºC;
- Tiredness;
- Difficulty feeding, in the case of infants.
These symptoms usually appear and disappear over several periods that can last for weeks or months.
Main causes
Bronchiolitis obliterans occurs when, due to some situation, there is an inflammatory reaction that results in infiltration in the bronchioles and alveoli, promoting irreversible airway obstruction. In most cases, this type of bronchitis is associated with infections, mainly by adenovirus. However, it can also happen as a consequence of infection by other types of viruses, such as the chickenpox or measles virus, or bacteria such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophilia and Bordetella pertussis.
Although most cases are due to infection by microorganisms, bronchiolitis obliterans can also occur due to diseases of the connective tissue, as a consequence of inhaling toxic substances or happen after bone marrow or lung transplantation.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of bronchiolitis obliterans should be made by the pediatric pulmonologist according to the signs and symptoms presented by the child, in addition to tests that help to identify the cause of bronchitis and its severity.
Thus, the doctor may recommend chest X-rays, computed tomography and lung scintigraphy, helping to differentiate bronchiolitis obliterans from other more common lung diseases. However, the definitive diagnosis can only be confirmed by lung biopsy.
How the treatment is done
The treatment aims to improve the child's respiratory capacity and, for this, the doctor may recommend the use of oral or inhaled anti-inflammatories and spray bronchodilators, which decrease the inflammation in the lungs and reduce the amount of mucus, decreasing the chances the appearance of new scars and facilitating the passage of air, in addition to oxygen therapy being recommended.
Respiratory physiotherapy may also be recommended in order to mobilize and facilitate the elimination of secretions, preventing the occurrence of other respiratory infections. Understand how respiratory physiotherapy is done.
In the case of patients with bronchiolitis obliterans develop infections in the course of the disease, the doctor may recommend the use of antibiotics according to the infectious agent responsible for the crises and exacerbations
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
Bibliography
- CASTRO-RODRIGUEZ, José A. et al. Postinfectious bronchiolitis obliterans in children: the S outh A merican contribution. Acta Paediatr. Vol 103. 9 ed; 913-921, 2014
- LASMAR, Laura Maria L. B. F et al. Post-infectious bronchiolitis obliterans: importance of early diagnosis and pediatric approach. Rev Med Minas Gerais. Vol 20. 3 ed; 44-51, 2010
- LINO, Carolina A. et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans: clinical and radiological profile of children followed up at a referral clinic. Rev Paul Pediatr. Vol 31. 1 ed; 10-16, 2013

.jpg)