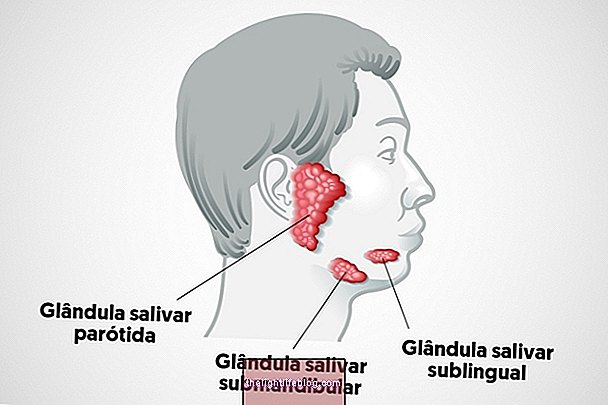
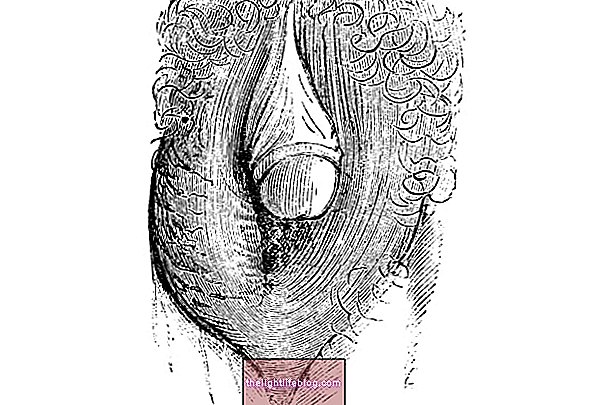
The dentigerous cyst is one of the most frequent cysts in dentistry and occurs when there is an accumulation of fluid between the structures of unerupted tooth formation such as the tooth enamel tissue and the crown, which is the part of the tooth that is exposed in the mouth. The tooth that is not erupted or included is one that is not born and has no position in the dental arch.
This cyst is more frequent in teeth called third molars, popularly called wisdom teeth, but it can also involve canine and premolar teeth.The wisdom tooth is the last tooth to be born, usually between 17 and 21 years of age, and its birth is slow and often painful, being in most cases recommended by the dentist to remove the tooth before its complete growth. Learn more about wisdom teeth.
The dentigerous cyst is more common in men between 10 and 30 years old, has slow growth, without symptoms and is not severe, and can be easily removed through a surgical procedure, according to the dentist's guidelines.

Main symptoms
The dentigerous cyst is usually small, asymptomatic and is only diagnosed on routine radiographic examinations. However, if there is an increase in size it can cause symptoms such as:
- Pain, being indicative of an infectious process;
- Local swelling;
- Numbness or tingling;
- Displacement of teeth;
- Discomfort;
- Deformity in the face.
The diagnosis of the dentigerous cyst is made by X-ray, but this examination is not always sufficient to complete the diagnosis, because on the radiograph the characteristics of the cyst are similar to other diseases, such as keratocyst and ameloblastoma, for example, which is a tumor that grows in the bones and mouth and causes symptoms when it is very large. Understand what ameloblastoma is and how the diagnosis is made.
How the treatment is done
The treatment for dentigerous cyst is surgical and can be through enucleation or marsupialization, which is chosen by the dentist depending on the person's age and size of the lesion.
Enucleation is usually the method of choice for the dentist and corresponds to the total removal of the cyst and the included tooth. If the dentist observes the possible eruption of the tooth, only partial removal of the cyst wall is performed, allowing the eruption. It is a definitive treatment without the need for other surgical procedures.
Marsupialization is done mainly for larger cysts or lesions that involve the jaw, for example. This procedure is less invasive, as it is performed to decrease the pressure inside the cyst by draining the liquid, thus decreasing the injury.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
-causas-e-como-tratar.jpg)