Neurofibromatosis, also known as Von Recklinghausen's disease, is a hereditary disease that manifests itself around the age of 15 and causes abnormal growth of nervous tissue in the body, forming small external tumors, called neurofibromas.
Neurofibromatosis is usually benign and can be divided into two groups:
- Neurofibromatosis type 1: caused by mutations in chromosome 17 that reduce the production of neurofibromin, a protein used by the body to prevent the onset of tumors. This type of neurofibromatosis can also cause loss of vision and impotence;
- Neurofibromatosis type 2: caused by mutations in chromosome 22, decreasing the production of merlina, another protein that suppresses the growth of tumors in healthy individuals. This type of neurofibromatosis can cause hearing loss.
Neurofibromatosis has no cure but can be treated with surgery and radiotherapy to decrease the number and size of tumors.
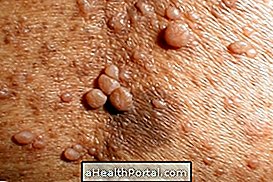

Symptoms of neurofibromatosis
Although it is a genetic disease, which is already born with the person, the symptoms can take years to manifest and not appear in the same way in all affected people.
The main symptom of neurofibromatosis is the appearance of soft tumors on the skin. However, depending on the type of neurofibromatosis, other symptoms are:
Neurofibromatosis type 1
- At least 6 coffee-colored spots with milk on the skin, approximately 0.5 cm;
- Sardines in the inguinal region and armpits noted up to 4 or 5 years;
- Small nodules under the skin, which arise at puberty;
- Small speckles in the iris of the eyes.
Neurofibromatosis type 2
- The appearance of small carobs on the skin, from adolescence;
- Gradual reduction of vision or hearing, with early cataract development;
- Difficulties of balance;
- Problems in the spine, such as scoliosis.
The diagnosis is made through the observation of the skin on the skin, and with x-rays, tomography and genetic blood tests, for example. This disease can also cause differences in the color between the two patient eyes, a change that is called heterochromia.
Learn more about identifying the disease in: Symptoms of neurofibromatosis.
How is the treatment?
Treatment for neurofibromatosis can be done through surgery to remove tumors that are causing pressure on organs or through radiotherapy to reduce their size. However, there is no treatment that guarantees cure or prevents the onset of new tumors.
In more severe cases where the patient develops cancer, treatment with chemotherapy or radiation therapy may be necessary for malignant tumors. Learn more about Treatment for neurofibromatosis.