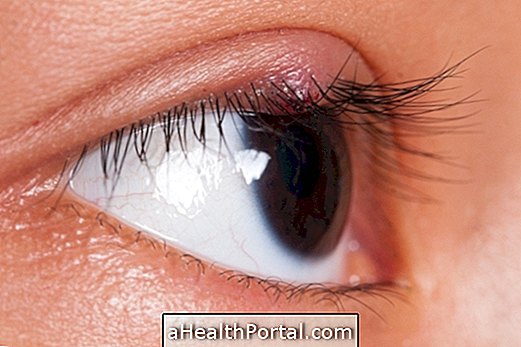
Blepharospasm, also known as benign essential blepharospasm, is a condition that occurs when one or both eyelids, the membrane over the eyes, are trembling and causes a reduction in the lubrication of the eyes and causes the person to blink more often. .
In most cases, blepharospasm is caused by excessive tiredness, spending too much time in front of the computer, excessive consumption of drinks and foods rich in caffeine, however, in some cases, when accompanied by other symptoms such as tremors in the body, for example, this condition can be a sign of some neurological disease such as Tourette's syndrome or Parkinson's disease.
Generally, blepharospasm disappears without needing specific treatment, but if it lasts more than a month, it is very frequent and causes the eyelid to relax, affecting vision, it is important to consult an ophthalmologist to indicate the most appropriate treatment.

Blepharospasm symptoms
Blepharospasm appears as a tremor in one or both eyelids, which may occur at the same time or not, and other symptoms may appear, such as:
- Dry eye;
- Increase in the amount of pis
- Involuntary closing of the eyes;
- Sensitivity to light;
- Irritability.
In addition, blepharospasm can also lead to facial spasms, which is when the face appears to be shaking as well, and ptosis of the eyelid can happen, which is when this skin falls over the eye.
Main causes
Blepharospasm is the condition that occurs when the eyelid is shaking, like a muscle spasm, and this is usually caused by insufficient sleep, excessive tiredness, stress, medication use, ingestion of caffeine-rich foods and drinks, such as coffee and soft drinks or for spending too much time in front of the computer or cell phone.
In some cases, the tremor in the eyelids of the eyes may be accompanied by swelling and redness of this area, which can be a sign of blepharitis, which is the inflammation of the edges of the eyelids. See how to identify blepharitis and which treatment is indicated.
When blepharospasm is associated with tremors in the body, it can indicate a problem in the cerebral control of muscles and this can happen in diseases such as Tourette's syndrome, Parkinson's, multiple sclerosis, dystonia or Bell's palsy.
How the treatment is done
Blepharospasm usually disappears without specific treatment, requiring only rest, reducing stressful situations and reducing the amount of caffeine in the diet, however, when symptoms are very frequent and do not go away after 1 month, it is important to see a general practitioner or neurologist.
During the consultation, an eyelid exam will be done and the doctor will be able to indicate medications such as muscle relaxants or anxiety medications, if the person is very anxious or stressed. In the most severe cases, the application of botox in very small amount, as this helps to relax the eyelid muscles and lessen the tremor.
Myectomy surgery may also be indicated, which is the surgical procedure that aims to remove some muscles and nerves from the eyelid, as this way, it is possible to relieve the tremor. Some complementary treatments can be done such as chiropractic, which is similar to therapeutic massages, and acupuncture, which is the application of very fine needles in the body. Check out what acupuncture is and what it is for.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
Bibliography
- THE JOHNS HOPKINS HOSPITAL. Blepharospasm. Available in: . Accessed on 21 Feb 2020
- UPTODATE. Classification and evaluation of dystonia. Available in: . Accessed on 21 Feb 2020
- NATIONAL EYE INSTITUTE. Blepharospasm. Available in: . Accessed on 21 Feb 2020
- AMERICAN ACADEMY OF FAMILY PHYSICIANS. Blepharospasm. Available in: . Accessed on 21 Feb 2020
- YEN, M. T. Blepharospasm and Hemifacial Spasm. International Ophthalmology Clinics. Vol.58, n.1. 1, 2018
- LEE, Seunghyun; PARK, Sangrye; LEW, Helen. Long-term Efficacy of Botulinum Neurotoxin-A Treatment for Essential Blepharospasm. Korean J Ophthalmol. Vol.32, n.1. 1-7, 2018
- LUCCI, Lucia M.D. Benign essential blepharospasm. Arq Bras Oftalmol. Vol.65. 585-589, 2002